Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2018; 24(34): 3834-3848
Published online Sep 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i34.3834
Published online Sep 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i34.3834
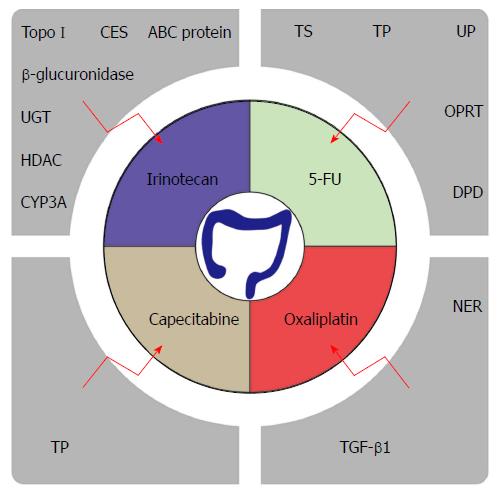
Figure 1 Potential mechanisms of resistance to chemotherapy agents.
In this schematic representation, the grey boxes highlight major contributors to chemotherapy resistance of irinotecan, 5-FU, capecitabine and oxaliplatin. TopoI: TopoisomeraseI; CES: Carboxylesterases; UGT: Uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase; CYP3A: Hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes; HDAC: Histone deacetylase; ABC protein: ATP-binding cassette transporter protein; TP: Thymidine phosphorylase; NER: Nucleotide excision repair; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor β1; TS: Thymidylate synthase; UP: Uridine phosphorylase; OPRT: Orotate phosphoribosyl transferase; DPD: Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Van der Jeught K, Xu HC, Li YJ, Lu XB, Ji G. Drug resistance and new therapies in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(34): 3834-3848
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i34/3834.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i34.3834