Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2018; 24(33): 3709-3723
Published online Sep 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i33.3709
Published online Sep 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i33.3709
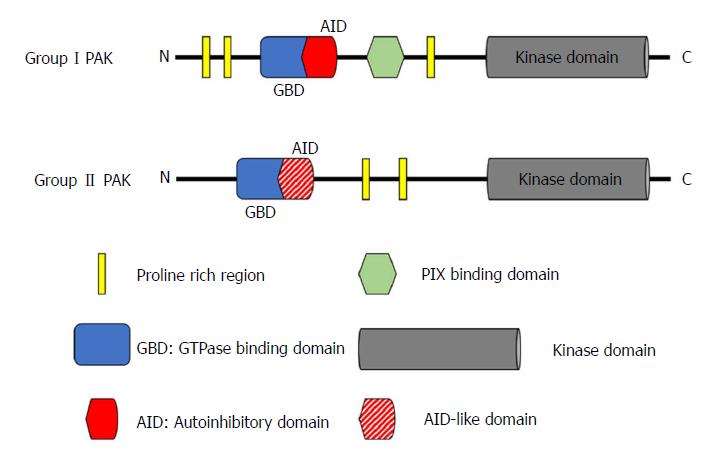
Figure 1 Structure of p21-activated kinases.
The six members of the PAK family can be divided by sequence and structural differences into two groups: Group I (PAK1-3) and group II (PAK4-6). All PAKs have an N-terminal regulatory domain and a conserved C-terminal serine/threonine kinase domain. In group I PAKs, the regulatory domain contains an AID, whereas group II PAKs (with the possible exception of PAK5) do not have a well-defined AID, but instead an AID-like domain. PIX: PAK-interactive exchange factor; PAK: p21-activated kinases; AID: Autoinhibitory domain; GBD: GTPase-binding domain.
- Citation: Wang K, Baldwin GS, Nikfarjam M, He H. p21-activated kinase signalling in pancreatic cancer: New insights into tumour biology and immune modulation. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(33): 3709-3723
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i33/3709.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i33.3709