Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2018; 24(32): 3650-3662
Published online Aug 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i32.3650
Published online Aug 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i32.3650
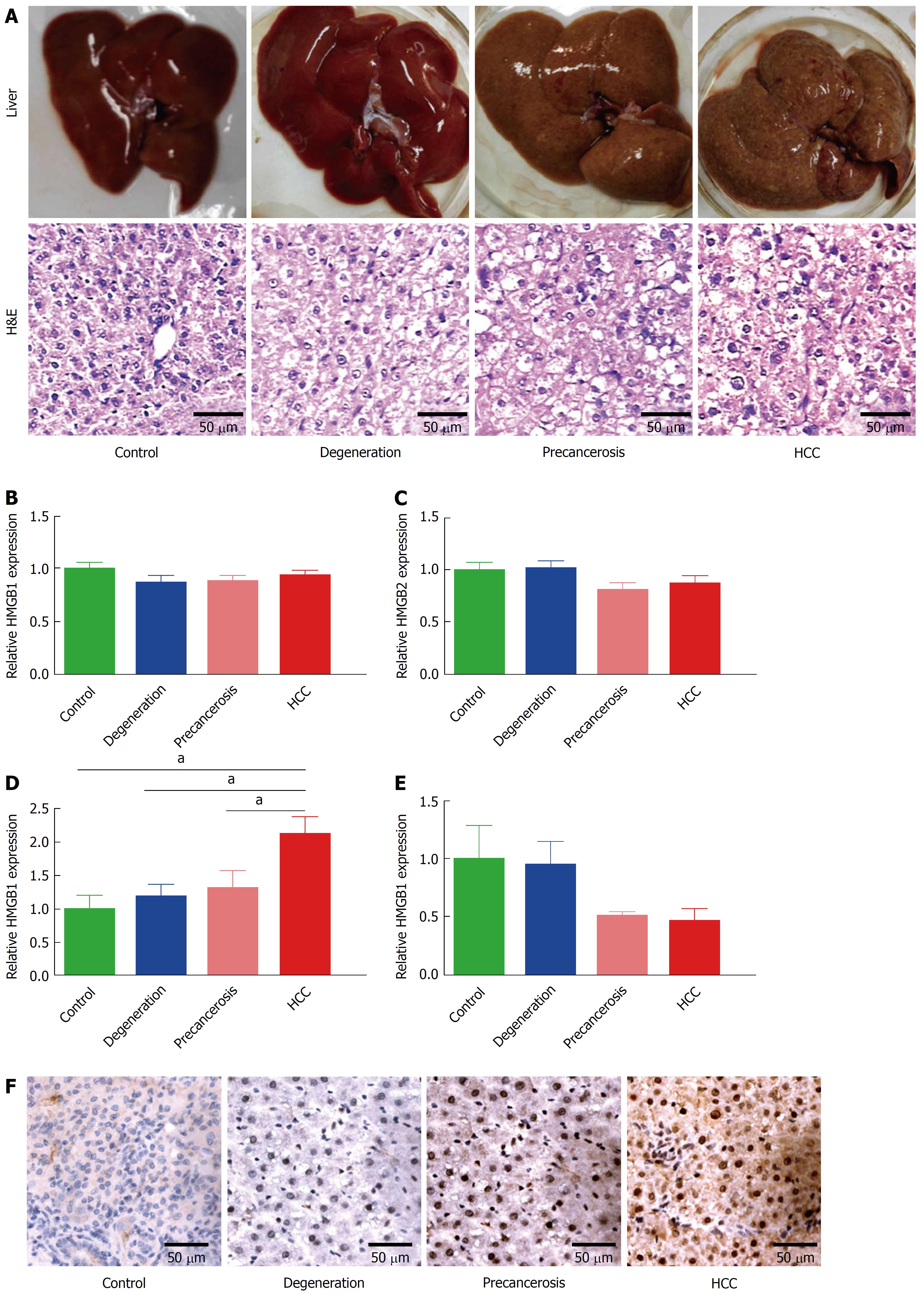
Figure 1 Dynamic upregulation of HMGB3 in rat hepatocarcinogenesis.
Rat hepatocarcinogenesis models were successfully made by consistent 2-AAF intake. A: The dynamic alterations of liver morphology (upper panel) and H&E staining (lower panel) of liver tissues in rat hepatocarcinogenesis. The livers of the rat model, according to the results of rat liver H&E staining, were divided into normal, degeneration, precancerous, and HCC group. B-E: the dynamic alterations of the HMGB family at the mRNA level in models were detected by RT-qPCR. B: HMGB1 mRNA. C: HMGB2 mRNA. D: HMGB3 mRNA. E: HMGB4 mRNA. Each band was presented as a relative value normalized to normal controls (n = 6). F: the immunohistochemical staining of rat HMGB3 expression in different groups. aP < 0.05. 2-AAF: 2-acetylaminofluorene; H&E: Hematoxylin and eosin; HMGB: High mobility group-box; RT-qPCR: Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
- Citation: Zheng WJ, Yao M, Fang M, Wang L, Dong ZZ, Yao DF. Abnormal expression of HMGB-3 is significantly associated with malignant transformation of hepatocytes. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(32): 3650-3662
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i32/3650.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i32.3650