Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2018; 24(31): 3488-3499
Published online Aug 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i31.3488
Published online Aug 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i31.3488
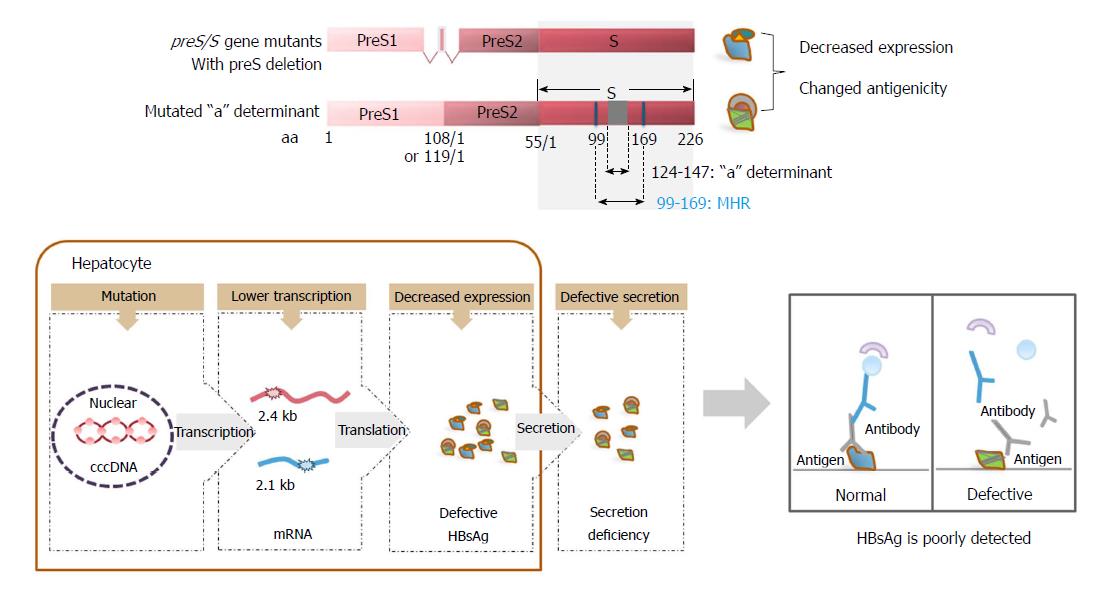
Figure 3 The relationship between the expression of defective surface antigens and occult hepatitis B virus infection.
Surface antigen mutations, such as preS deletions, can impair the transcription of 2.4 and 2.1 kb HBV RNAs, leading to decreased levels of three HBV surface proteins. In addition, defective surface antigens with preS deletions and mutations within the “a” determinant are secretion deficient. Single or multiple mutations occurring within the MHR between the aa residues 99-169 of SHBs, especially those within the “a” determinant between aa 124-147, can lead to conformational changes of HBsAg. Mutated HBsAg is poorly detected by immunoassays based on monoclonal antibodies, contributing to some cases of OBI. OBI: Occult hepatitis B virus infection; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen.
- Citation: Wu CC, Chen YS, Cao L, Chen XW, Lu MJ. Hepatitis B virus infection: Defective surface antigen expression and pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(31): 3488-3499
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i31/3488.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i31.3488