Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2018; 24(31): 3488-3499
Published online Aug 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i31.3488
Published online Aug 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i31.3488
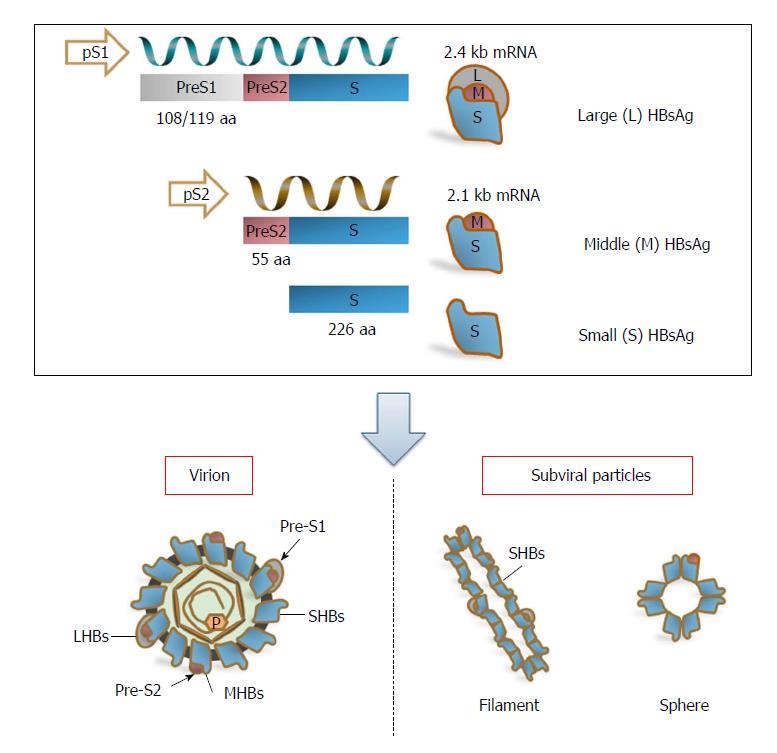
Figure 1 The transcription and expression of hepatitis B virus surface proteins.
The three HBV surface proteins, LHBs, MHBs, and SHBs, are translated from two different mRNAs: LHBs are encoded by the preS1 promoter-initiated 2.4 kb subgenomic RNA; MHBs and SHBs are encoded by the preS2 promoter-initiated 2.1 kb subgenomic RNA. The 2.4 and 2.1 kb subgenomic RNAs share the same 3’ end and only differ in length due to differences at the 5’ end, which lead to different amino-terminal but identical carboxy-terminal regions of the three surface antigens. Therefore, LHBs contain preS1 + preS2 + S (389 or 400 aa residues), MHBs contain preS2 + S (281 aa residues), and SHBs contain the S domain (226 aa residues) alone. For mature/infectious virions, LHBs, MHBs, and SHBs are present in the envelopes at a ratio of approximately 1:1:4. In addition, the major fraction of SHBs forms subviral particles (filaments and spheres) together with the minor parts of LHBs and/or MHBs. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; LHBs: Large surface antigens; MHBs: Middle surface antigens; SHBs: Small surface antigens.
- Citation: Wu CC, Chen YS, Cao L, Chen XW, Lu MJ. Hepatitis B virus infection: Defective surface antigen expression and pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(31): 3488-3499
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i31/3488.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i31.3488