Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2018; 24(3): 387-396
Published online Jan 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i3.387
Published online Jan 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i3.387
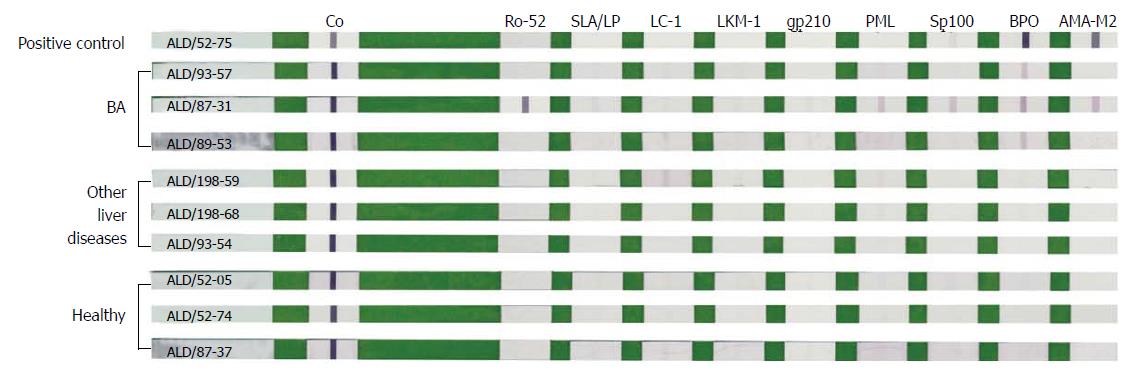
Figure 1 Representative strips after color development by line-blot immunoassay.
The line-blot immunoassay strips had been coated with nine autoimmune liver disease-related antigens, including Ro-52, SLA/LP, LC-1, LKM-1, gp210, PML, Sp100, BPO and AMA-M2 (from left to right). BA group: ALD/93-57 with anti-BPO +; ALD/87-31 with anti-Ro-52 +++, anti-PML +, anti-Sp100 +, anti-BPO ++, and AMA-M2 +; ALD/89-53 with anti-BPO +; Other liver diseases group: Only ALD/198-59 with anti-LC-1 ±; Healthy group: All autoantibodies were negative. Positive control (ALD/52-75) showed anti-BPO +++ and AMA-M2 +++. Other liver diseases include choledochal cysts, transient cholestasis of unknown origin, and neonatal intrahepatic cholestasis caused by citrin deficiency. ALD: Autoimmune liver disease; BA: Biliary atresia; LC-1: Liver cytosolic antigen type 1.
- Citation: Pang SY, Dai YM, Zhang RZ, Chen YH, Peng XF, Fu J, Chen ZR, Liu YF, Yang LY, Wen Z, Yu JK, Liu HY. Autoimmune liver disease-related autoantibodies in patients with biliary atresia. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(3): 387-396
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i3/387.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i3.387