Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2018; 24(29): 3260-3272
Published online Aug 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i29.3260
Published online Aug 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i29.3260
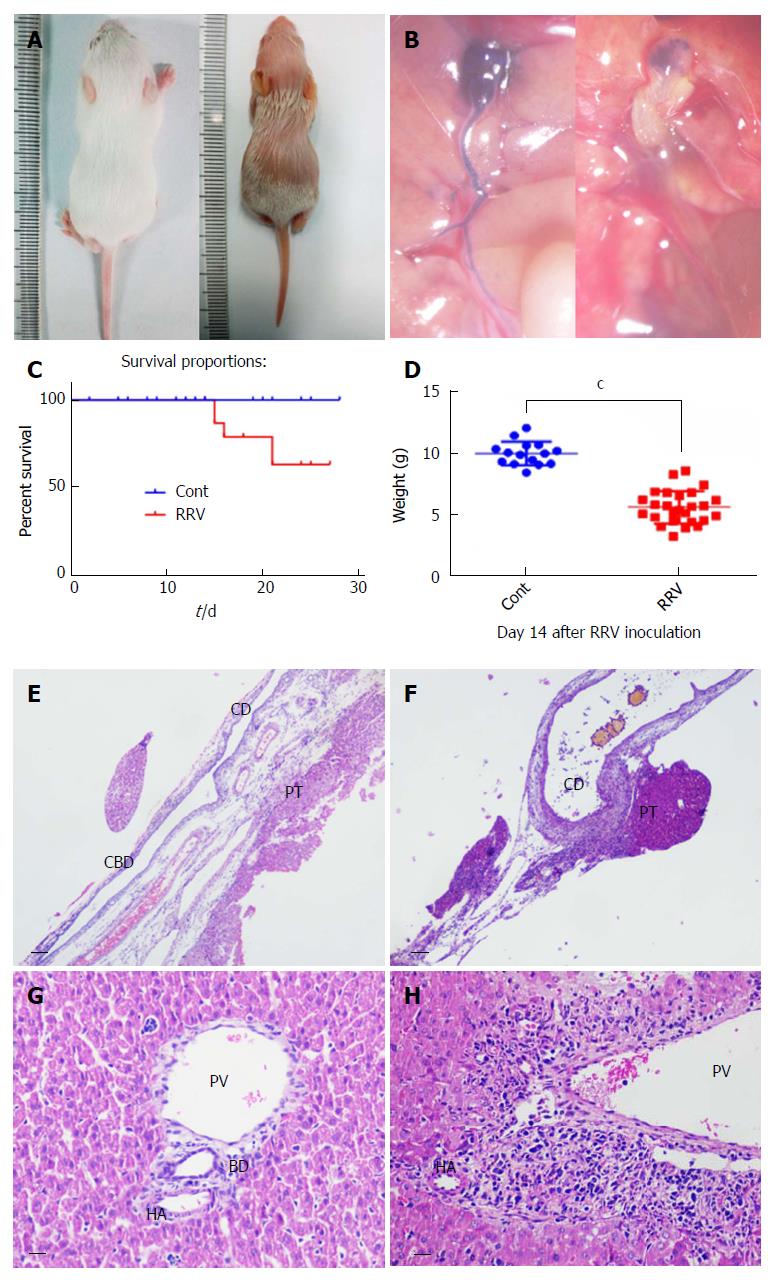
Figure 2 Biliary atresia in neonatal mice with a low dose of rhesus rotavirus inoculation.
To study the expression levels of the components of the Notch signaling pathway in the biliary atresia (BA) animal model, a lower dose of 20 μL of rhesus rotavirus (RRV) with a titer of 4 × 104 PFU/mL was used. The morphology and extrahepatic block were photographed (A and B). The survival rate was measured at 21 d after viral inoculation (C). BA syndrome was observed between days 5 and 6. The body weights of the mice were measured at day 14 and compared with that of the control group (injected with culture supernatant but no virus) (D) (P < 0.001, n = 15 in the Cont. group, and n = 26 in the RRV group). After dissection, the portal triad (E and F) and liver tissue at day 14 (G and H) were sectioned, and histological analysis was performed. The scale bar is shown as 0.2 mm in the portal triad sections and as 50 μm in the liver tissue sections. CD: Cystic duct; CBD: Common bile duct; PT: Portal triad; PV: Portal vein; HA: Hepatic artery; BD: Bile duct.
- Citation: Zhang RZ, Zeng XH, Lin ZF, Ming-Fu, Tong YL, Lui VC, Tam PK, Lamb JR, Xia HM, Chen Y. Downregulation of Hes1 expression in experimental biliary atresia and its effects on bile duct structure. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(29): 3260-3272
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i29/3260.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i29.3260