Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2018; 24(28): 3130-3144
Published online Jul 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i28.3130
Published online Jul 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i28.3130
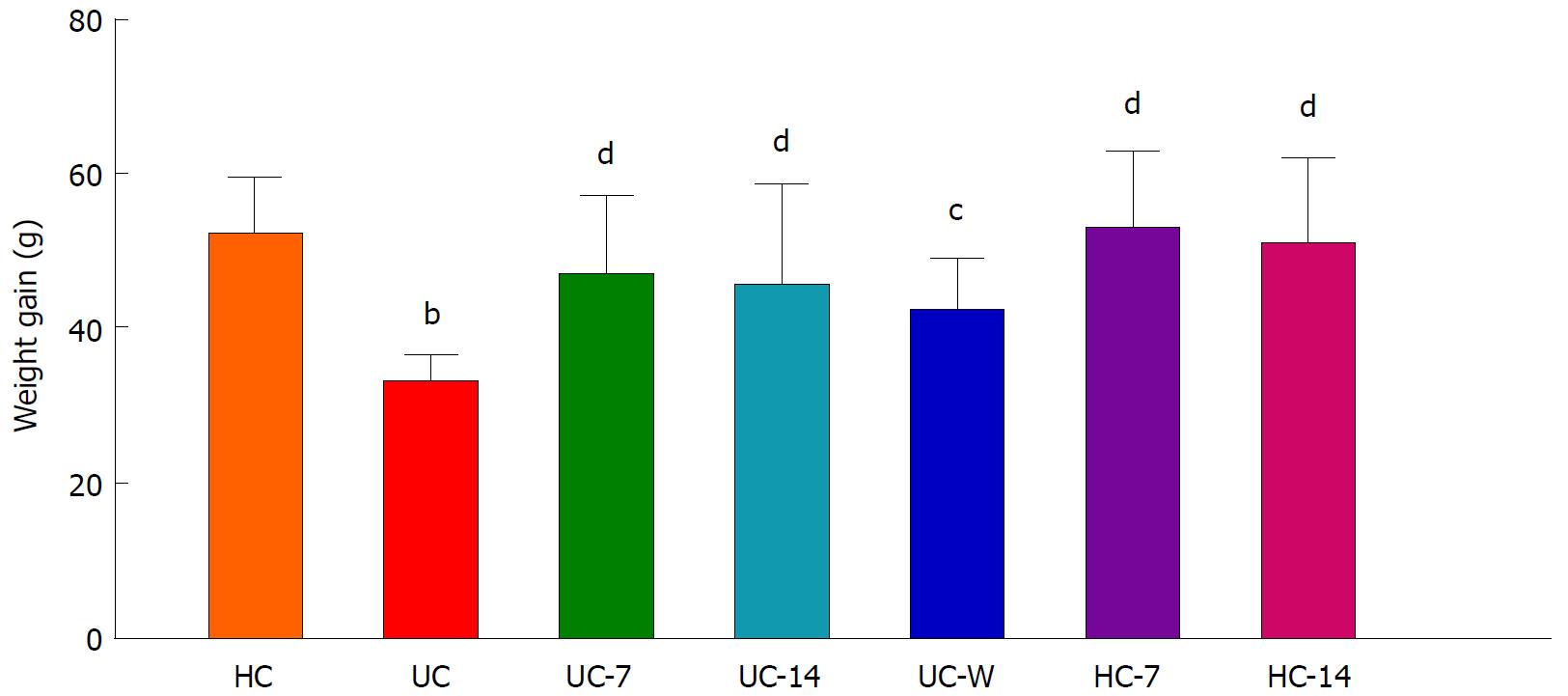
Figure 1 Body weight gains after treatment in different groups.
HC: Healthy controls; UC: UC model group; UC-7: UC model with seven days of moxibustion; UC-14: UC model with fourteen days of moxibustion; UC-W: UC model with mesalazine gavage; HC-7: Healthy controls with seven days of moxibustion; HC-14: healthy controls with fourteen days of moxibustion. The body weight gain in the UC group was decreased compared with the HC group (P < 0.01). After treatment, the body weight gains in the UC-7, UC-14, HC-7, HC-14 (P < 0.01) and UC-W (P < 0.05) groups were increased compared with the UC group. bP < 0.01 vs the HC group; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs the UC group.
- Citation: Qi Q, Liu YN, Jin XM, Zhang LS, Wang C, Bao CH, Liu HR, Wu HG, Wang XM. Moxibustion treatment modulates the gut microbiota and immune function in a dextran sulphate sodium-induced colitis rat model. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(28): 3130-3144
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i28/3130.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i28.3130