Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2018; 24(28): 3120-3129
Published online Jul 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i28.3120
Published online Jul 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i28.3120
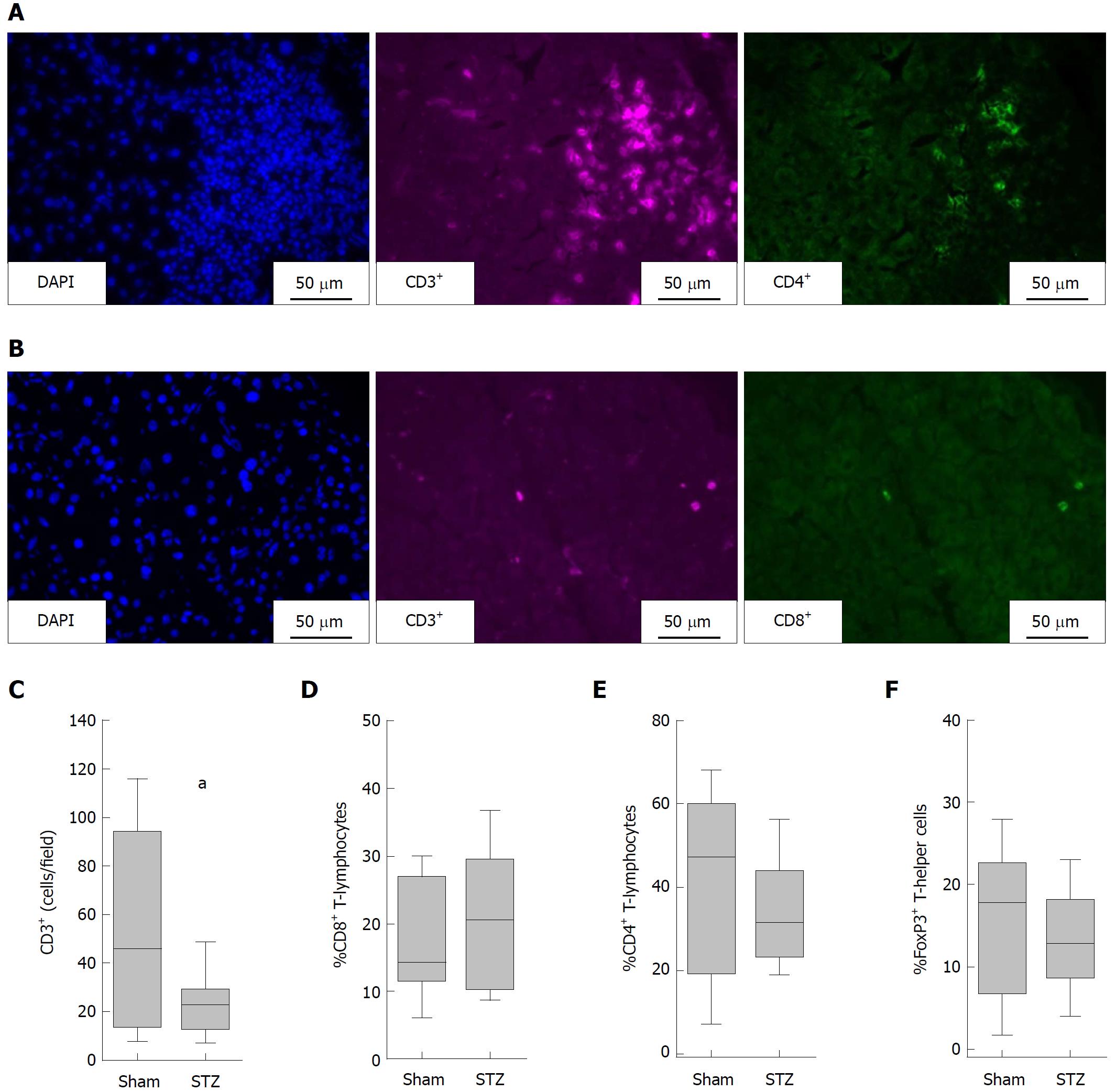
Figure 3 Evaluation of the local pancreatic inflammation during autoimmune pancreatitis.
Representative images of T-helper cells (CD3+CD4+cells) (A); and cytotoxic T-cells (CD3+CD8+ cells) (B); hyperglycemia induced by STZ decreased the number of T-lymphocytes (defined as number of CD3+ per field) (C); little differences are observed in the percentage of cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CD8+CD3+ cells × 100 divided by the number of CD3+cells) (D); T-helper cells (CD4+CD3+ cells × 100 divided by the number of CD3+cells) (E); and regulatory T-cells (FoxP3+CD4+cells × 100 divided by the number of CD4+ cells) (F). The number of animals evaluated was n = 19 (Sham) and n = 17 (STZ). Differences between the indicated cohorts are indicated as tendency, aP = 0.053. STZ: Streptozotocin-treated.
- Citation: Müller-Graff FT, Fitzner B, Jaster R, Vollmar B, Zechner D. Impact of hyperglycemia on autoimmune pancreatitis and regulatory T-cells. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(28): 3120-3129
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i28/3120.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i28.3120