Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2018; 24(26): 2867-2877
Published online Jul 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i26.2867
Published online Jul 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i26.2867
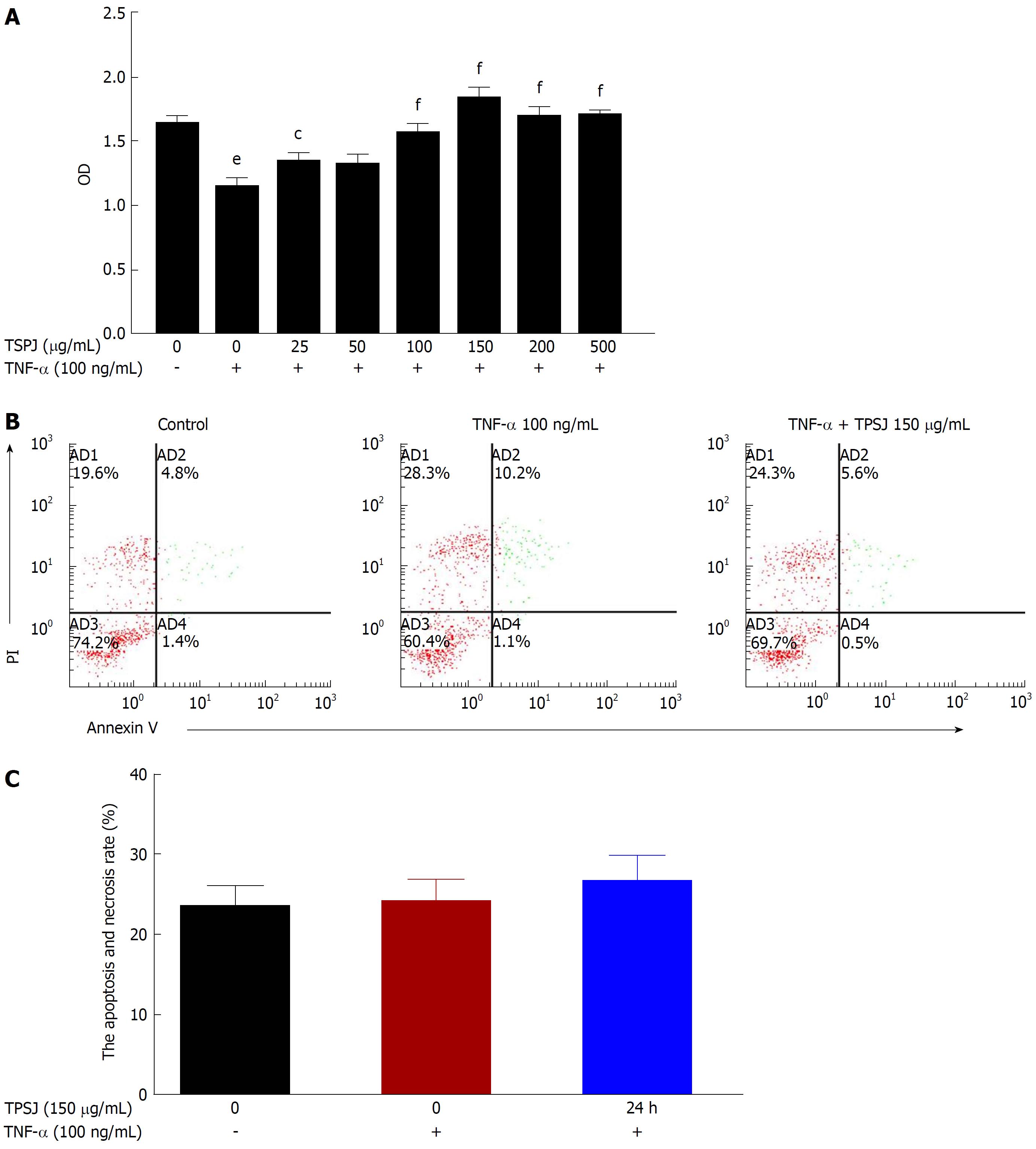
Figure 2 Total polysaccharides of the Sijunzi decoction promoted the proliferation of tumor necrosis factor-α-damaged Caco-2 cells.
A: Caco-2 cells were treated with various concentrations of TPSJ (25-500 μg/mL) or control DMEM for 24 h. The effect of TPSJ on cell viability was measured using the MTT assay; B: TNF-α-damaged Caco-2 cells were incubated with 150 μg/mL TPSJ or control DMEM for 24 h. The induction of apoptosis was determined using an Annexin V-FITC/propidium iodide staining assay; C: Quantification of the numbers of apoptotic and necrotic cells. Data are shown as the means ± standard errors of the means of at least three independent experiments (eP < 0.001 vs control Caco-2 cells; cP < 0.05, fP < 0.001 vs TNF-α-damaged Caco-2 cells). TPSJ: Total polysaccharides of the Sijunzi decoction; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; DMEM: Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium; MTT: 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide.
- Citation: Lu Y, Li L, Zhang JW, Zhong XQ, Wei JA, Han L. Total polysaccharides of the Sijunzi decoction attenuate tumor necrosis factor-α-induced damage to the barrier function of a Caco-2 cell monolayer via the nuclear factor-κB-myosin light chain kinase-myosin light chain pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(26): 2867-2877
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i26/2867.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i26.2867