Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2018; 24(24): 2617-2627
Published online Jun 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i24.2617
Published online Jun 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i24.2617
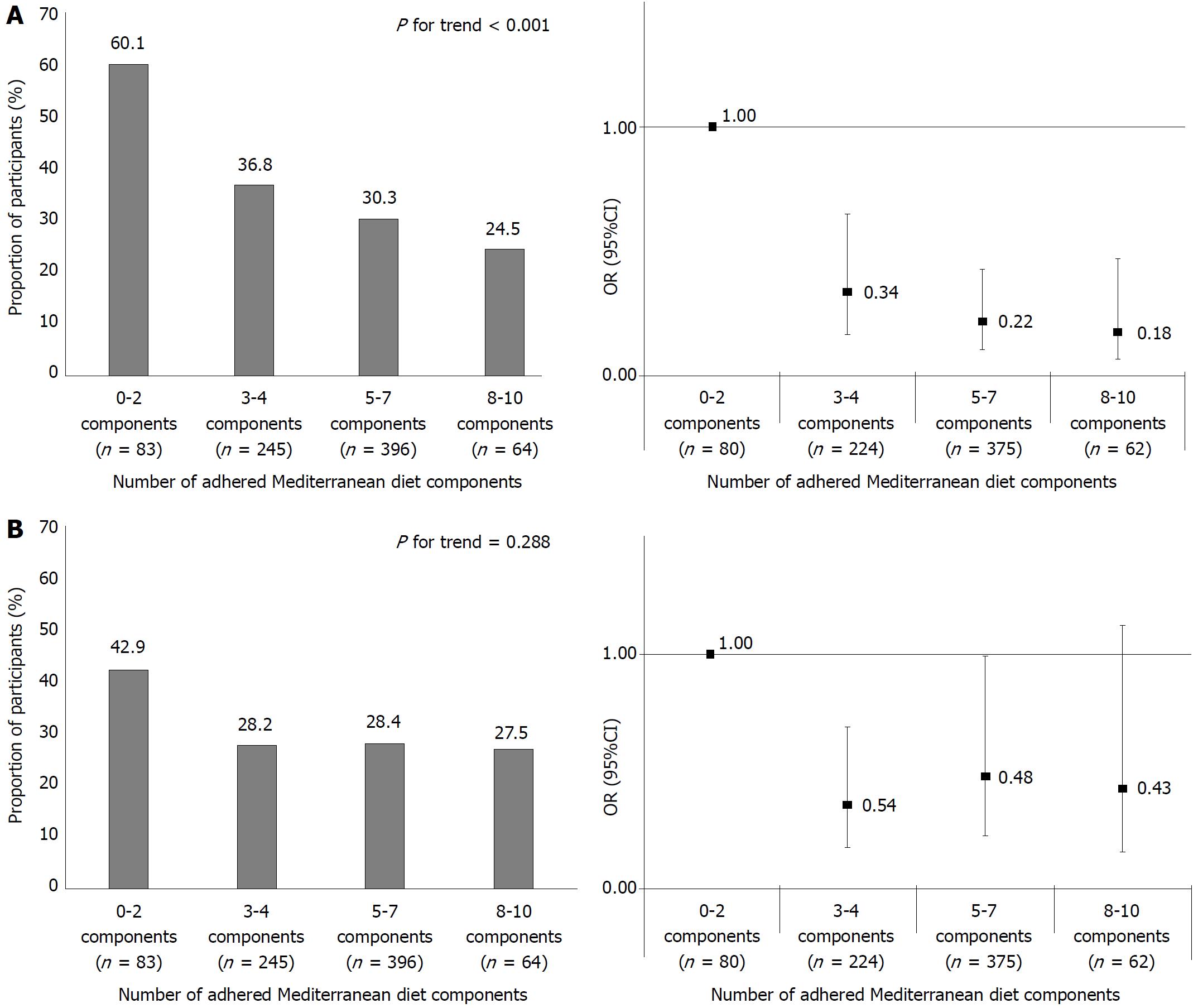
Figure 1 Dose response univariate and multivariate association between the number of adhered Mediterranean dietary components and (A) advanced colorectal polyps or (B) non-advanced adenomas.
Association between the number of adhered Mediterranean dietary components and (A) advanced polyps, univariate (left panel) and multivariate (right panel) or (B) non-advanced adenomas, univariate (left panel) and multivariate (right panel). Univariate P-values are calculated by Chi-Square test. OR adjusted for: Age (years), gender, smoking (ever), BMI (kg/m2), use of aspirin, NSAIDs, statin and antidiabetic medication, daily caloric intake (kcal) and colonoscopy indication (screening, diagnostic or surveillance), and 95%CI are calculated by logistic regression. BMI: Body mass index; NSAIDS: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Citation: Fliss-Isakov N, Kariv R, Webb M, Ivancovsky D, Margalit D, Zelber-Sagi S. Mediterranean dietary components are inversely associated with advanced colorectal polyps: A case-control study. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(24): 2617-2627
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i24/2617.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i24.2617