Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2018; 24(2): 226-236
Published online Jan 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i2.226
Published online Jan 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i2.226
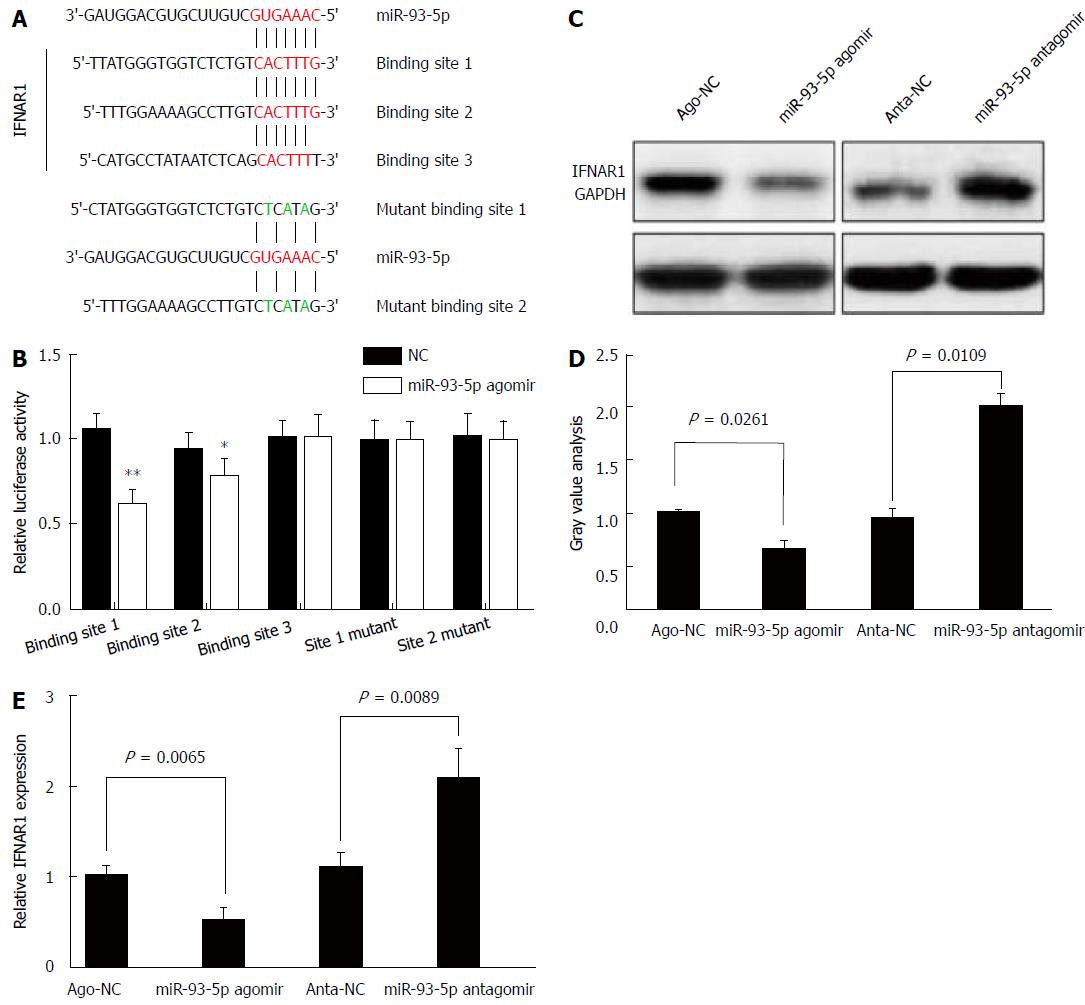
Figure 4 FNAR1 is a direct target of miR-93-5p .
A: The binding sites for miR-93-5p in the IFNAR1 3’-UTR, and the design of mutant binding sites in the IFNAR1 3’-UTR for miR-93-5p; B: Luciferase assay shows that miR-93-5p agomir inhibits the relative luciferase activity in the binding site 1 or 2-expressing HEK293T cells, but not in the binding site 3- or mutant binding sites-expressing HEK293T cells. This experiment was repeated six times; C and D: Western blot shows the protein expression of IFNAR1 in Huh7 cells transfected with ago-NC (200 nmol/L), miR-93-5p agomir (200 nmol/L), anta-NC (200 nmol/L), and miR-93-5p antagomir (200 nmol/L). This experiment was repeated twice; E: qRT-PCR shows the mRNA expression of IFNAR1 in Huh7 cells transfected with ago-NC (200 nmol/L), miR-93-5p agomir (200 nmol/L), anta-NC (200 nmol/L), and miR-93-5p antagomir (200 nmol/L). β-actin was used as an internal reference. This experiment was repeated three times. IFNAR1: Interferon receptor 1.
- Citation: He CL, Liu M, Tan ZX, Hu YJ, Zhang QY, Kuang XM, Kong WL, Mao Q. Hepatitis C virus core protein-induced miR-93-5p up-regulation inhibits interferon signaling pathway by targeting IFNAR1. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(2): 226-236
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i2/226.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i2.226