Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2018; 24(2): 226-236
Published online Jan 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i2.226
Published online Jan 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i2.226
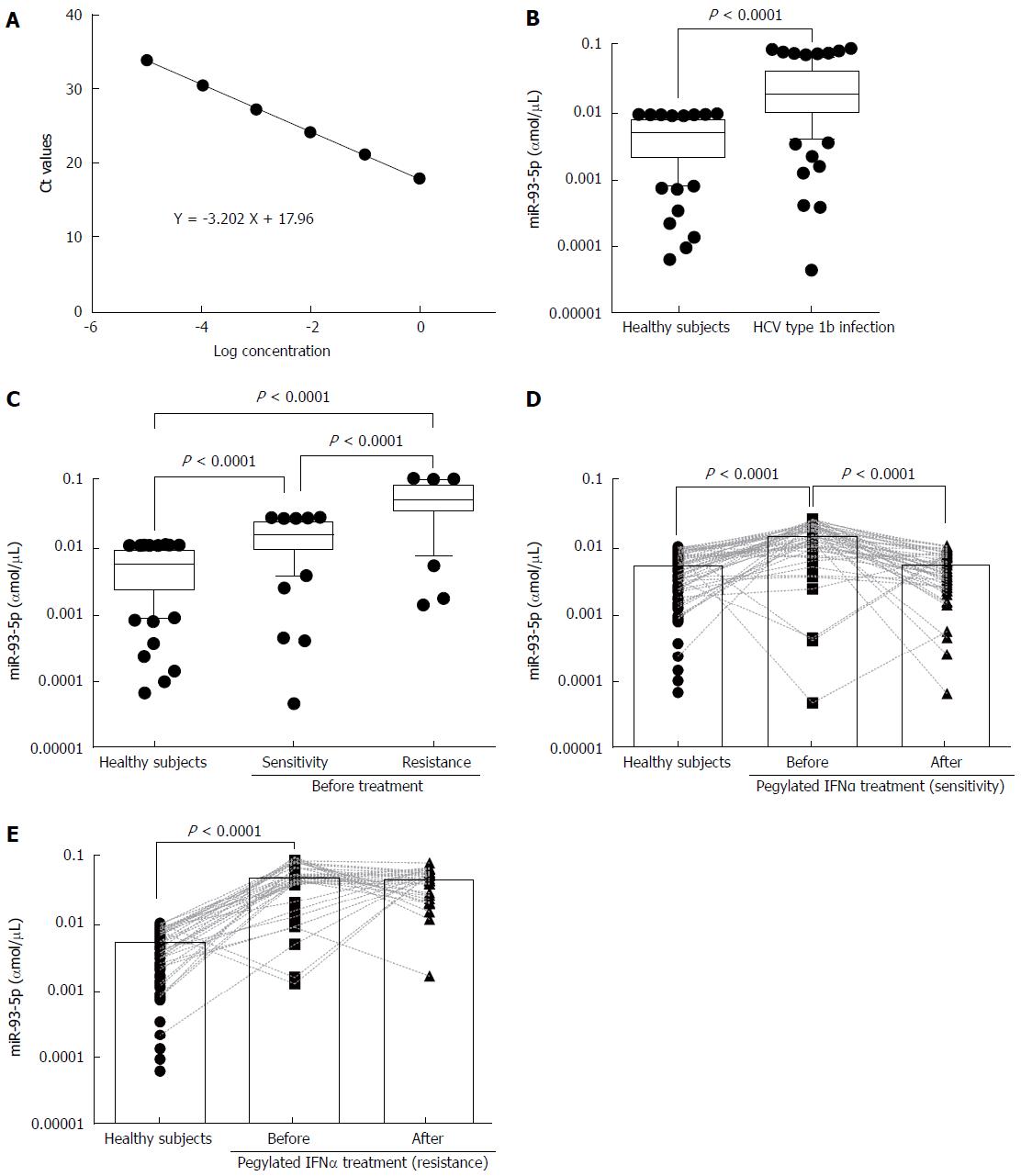
Figure 1 Serum miR-93-5p expression is increased in hepatitis C virus-1b-infected patients.
A: The linearity of miR-93-5p quantification; B: Box shows serum miR-93-5p concentrations in 84 patients with HCV-1b infection, compared with 84 healthy subjects; C: Box shows serum miR-93-5p concentrations in 50 HCV-1b-infected patients with pegylated IFNα sensitivity and 34 HCV-1b-infected patients with pegylated IFNα resistance, compared with 84 healthy subjects; D: Scatter shows serum miR-93-5p concentrations in 84 healthy subjects and 50 HCV 1b-infected patients with pegylated IFNα sensitivity before or after treatment; E: Scatter shows serum miR-93-5p concentrations in 84 healthy subjects and 34 HCV 1b-infected patients with pegylated IFNα resistance before or after treatment. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; IFNα: Interferon-α.
- Citation: He CL, Liu M, Tan ZX, Hu YJ, Zhang QY, Kuang XM, Kong WL, Mao Q. Hepatitis C virus core protein-induced miR-93-5p up-regulation inhibits interferon signaling pathway by targeting IFNAR1. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(2): 226-236
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i2/226.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i2.226