Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2018; 24(2): 170-178
Published online Jan 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i2.170
Published online Jan 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i2.170
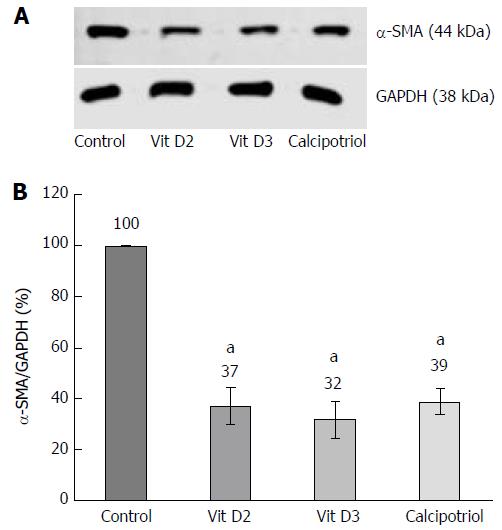
Figure 3 D-vitamins reduce protein levels of α-smooth muscle actin in primary cultured pancreatic stellate cells.
Pancreatic stellate cells were treated with the indicated D-vitamins (100 nmol/L each) from day 1-4 of primary culture, before expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and the housekeeping protein GAPDH was assessed by Western blot analysis (see A for a typical experiment); B: Intensities of fluorescence signals were expressed as ratio α-SMA/GAPDH. Data of 5 independent experiments were used to calculate mean ± SE. aP < 0.05 vs untreated controls.
- Citation: Wallbaum P, Rohde S, Ehlers L, Lange F, Hohn A, Bergner C, Schwarzenböck SM, Krause BJ, Jaster R. Antifibrogenic effects of vitamin D derivatives on mouse pancreatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(2): 170-178
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i2/170.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i2.170