Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2018; 24(19): 2047-2060
Published online May 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i19.2047
Published online May 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i19.2047
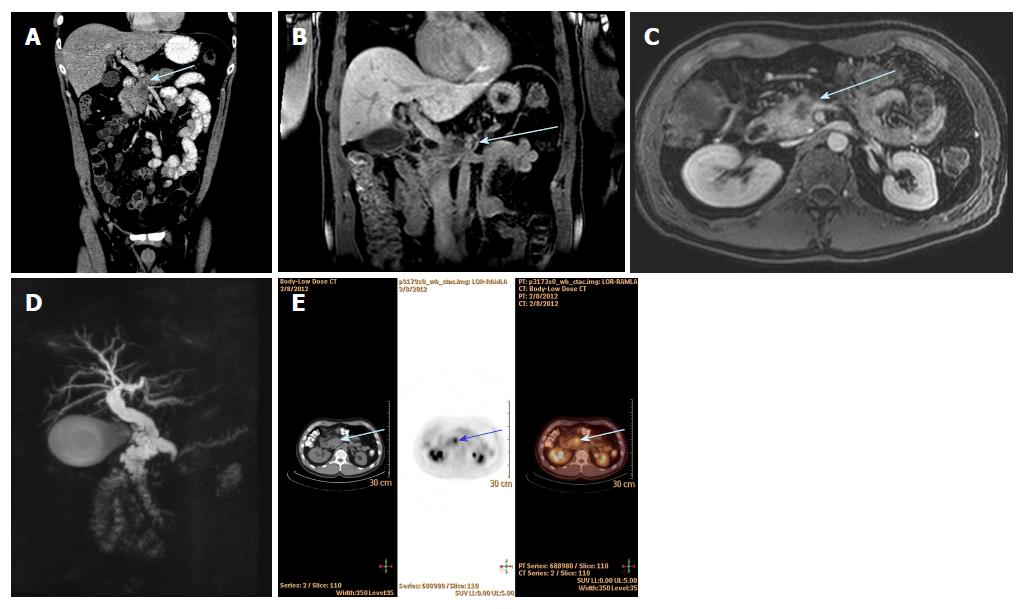
Figure 3 Multimodal imaging techniques utilised for a patient with 2.
8 cm head of pancreas cancer (blue arrow) with portal vein and superior mesenteric vein invasion. A: Hypodense mass on coronal view on CT; B: T1-weighted coronal view on MRI; C: T1-weighted axial view on MRI; D: MRCP view with dilated CBD and PD (double duct sign); E: Axial view on PET CT imaging showing marked FDG avidity. CT: Computed tomography; MDCT: Multi-detector computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; PET: Positron emission tomography; MRCP: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography; FDG: Fluorodeoxyglucose.
- Citation: Zhang L, Sanagapalli S, Stoita A. Challenges in diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(19): 2047-2060
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i19/2047.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i19.2047