Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2018; 24(18): 1995-2008
Published online May 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i18.1995
Published online May 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i18.1995
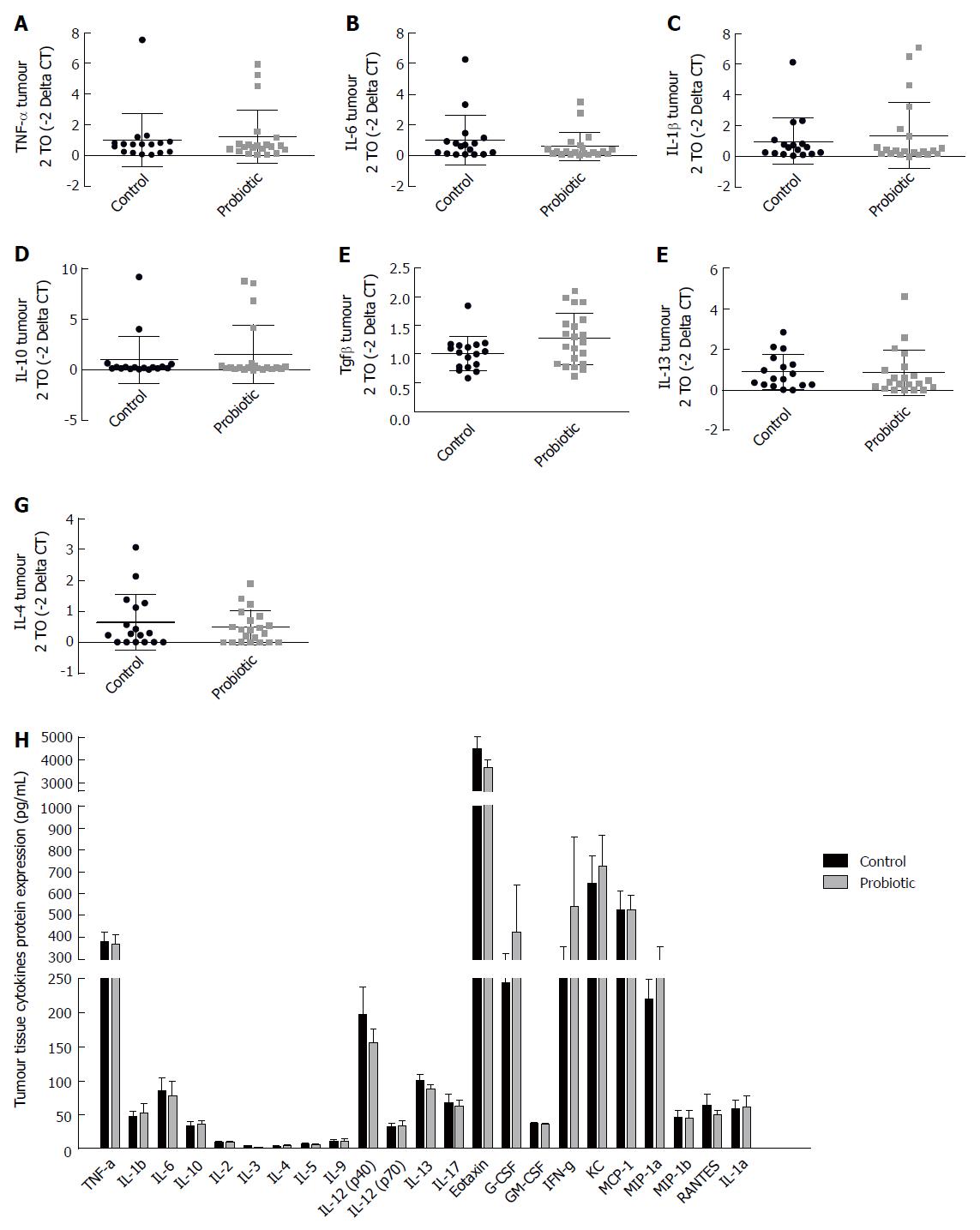
Figure 5 Probiotic supplementation does not modify the tumour microenvironment.
Real-time RT-PCR analysis of TNF-α (A), IL-6 (B), IL-1β (C), IL-10 (D), TGF-β1 (E), and IL-13 (F), IL-4(G) in colon tumour tissue of control and probiotic groups; results are presented relative to those of Gapdh. H: Concentration of cytokines in the tumour tissue analysed by Bio-Plex Multiplex cytokine assay at day 60 after injection with azoxymethane. Mann-Whitney U test. Data from two independent experiments, presented as mean and standard deviation.
- Citation: Mendes MCS, Paulino DS, Brambilla SR, Camargo JA, Persinoti GF, Carvalheira JBC. Microbiota modification by probiotic supplementation reduces colitis associated colon cancer in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(18): 1995-2008
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i18/1995.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i18.1995