Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2018; 24(17): 1901-1910
Published online May 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1901
Published online May 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1901
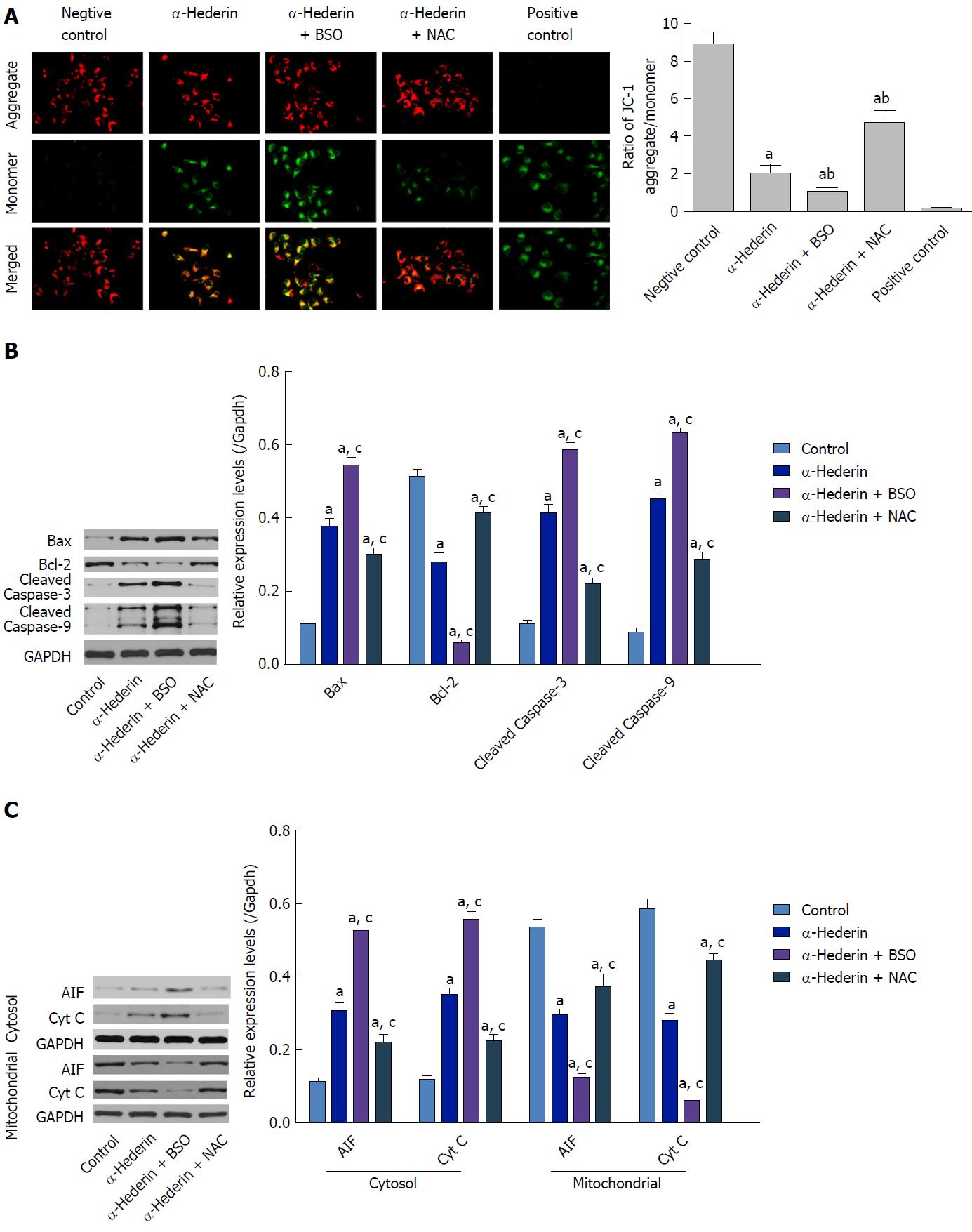
Figure 3 α-hederin induces apoptosis through activation of the mitochondria-mediated pathway.
A: Mitochondrial membrane potential was detected with JC-1. JC-1 aggregates (red fluorescence) under conditions of a normal mitochondrial membrane and forms a monomer (green fluorescence) under depolarizing conditions. Fluorescence was detected by a confocal laser scanning microscope (400 ×); B and C: Western blots showing the expression of mitochondrial pathway-related proteins in vitro. SMMC-7721 cells were treated with α-hederin (0 or 10 μmol/L) with or without BSO (2 mmol/L) or NAC (5 mmol/L) pretreatment, and the protein levels of Bcl-2, Bax, caspase-9, caspase-3, AIF, and Cyt C in SMMC-7721 cells were then detected by western blotting. GAPDH expression was used as an internal control. The relative expression levels of these proteins in SMMC-7721 cells in different groups were compared. aP < 0.05 vs control; cP < 0.05 vs α-hederin (10 μmol/L). AIF: Apoptosis-inducing factor; ATP: adenosine triphosphate; BSO: DL-buthionine-S,R-sulfoximine; Cyt C: Cytochrome C; NAC: N-acetylcysteine.
- Citation: Li J, Wu DD, Zhang JX, Wang J, Ma JJ, Hu X, Dong WG. Mitochondrial pathway mediated by reactive oxygen species involvement in α-hederin-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(17): 1901-1910
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i17/1901.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1901