Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2018; 24(17): 1888-1900
Published online May 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1888
Published online May 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1888
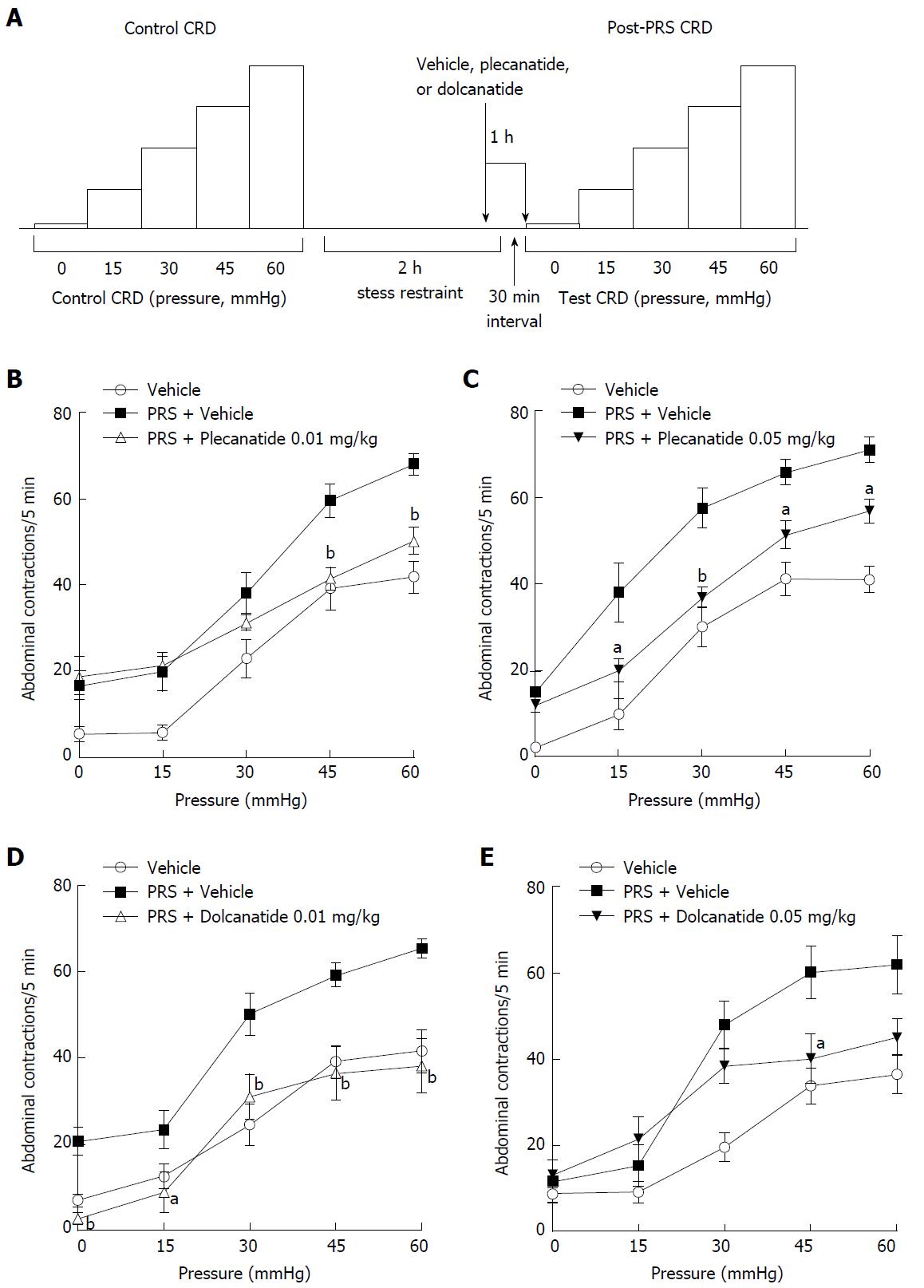
Figure 6 Design and results of the partial restraint stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity models.
A: Schematic depicting the sequence of test sessions and treatments to evaluate visceral hypersensitivity induced by PRS in rat models. Effects of oral administration of plecanatide, dolcanatide or vehicle on the increase in abdominal contractions to CRD when tested 30 min after a two h period of partial restraint. Doses of 0.01 and 0.05 mg/kg of plecanatide (B and C) or dolcanatide (D and E) 30 min before completion of the restraint session reduced the rate of muscular contractions toward the levels observed in a previous test session without exposure to partial restraint. Data are the mean ± SEM (n = 8 rats/group). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 as compared to the values for PRS + vehicle control. CRD: Colorectal distention; PRS: Partial restraint stress; SEM: Standard error of the mean.
- Citation: Boulete IM, Thadi A, Beaufrand C, Patwa V, Joshi A, Foss JA, Eddy EP, Eutamene H, Palejwala VA, Theodorou V, Shailubhai K. Oral treatment with plecanatide or dolcanatide attenuates visceral hypersensitivity via activation of guanylate cyclase-C in rat models. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(17): 1888-1900
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i17/1888.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1888