Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2018; 24(17): 1888-1900
Published online May 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1888
Published online May 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1888
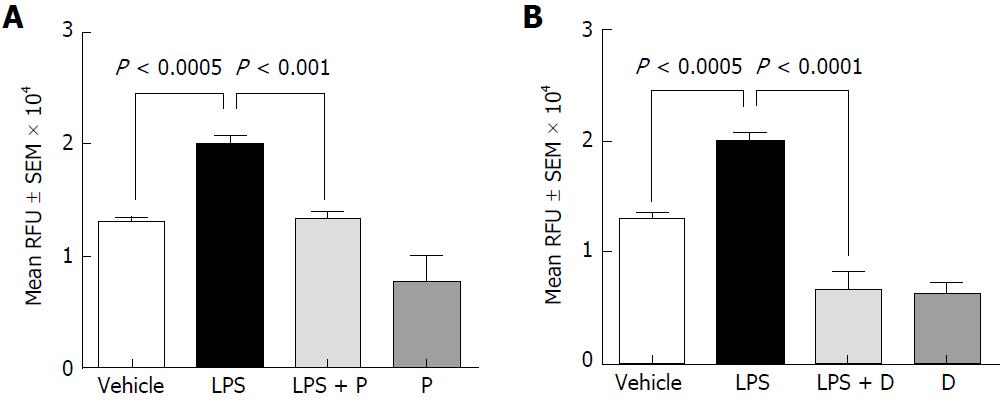
Figure 2 Effect of plecanatide (A) and dolcanatide (B) on lipopolysaccharide-induced increased permeability of 4 kD fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran across rat colon tissues.
Rat colon tissues (2 cm pieces) were incubated overnight with vehicle, 10 μM plecanatide or dolcanatide in the presence or absence of 100 μg/mL LPS. Data represent mean fluorescence ± SEM recorded 75 min after the addition of FITC-dextran. D: Dolcanatide; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; P: Plecanatide; RFU: Relative fluorescence units; SEM: Standard error of the mean.
- Citation: Boulete IM, Thadi A, Beaufrand C, Patwa V, Joshi A, Foss JA, Eddy EP, Eutamene H, Palejwala VA, Theodorou V, Shailubhai K. Oral treatment with plecanatide or dolcanatide attenuates visceral hypersensitivity via activation of guanylate cyclase-C in rat models. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(17): 1888-1900
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i17/1888.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1888