Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2018; 24(17): 1839-1858
Published online May 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1839
Published online May 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1839
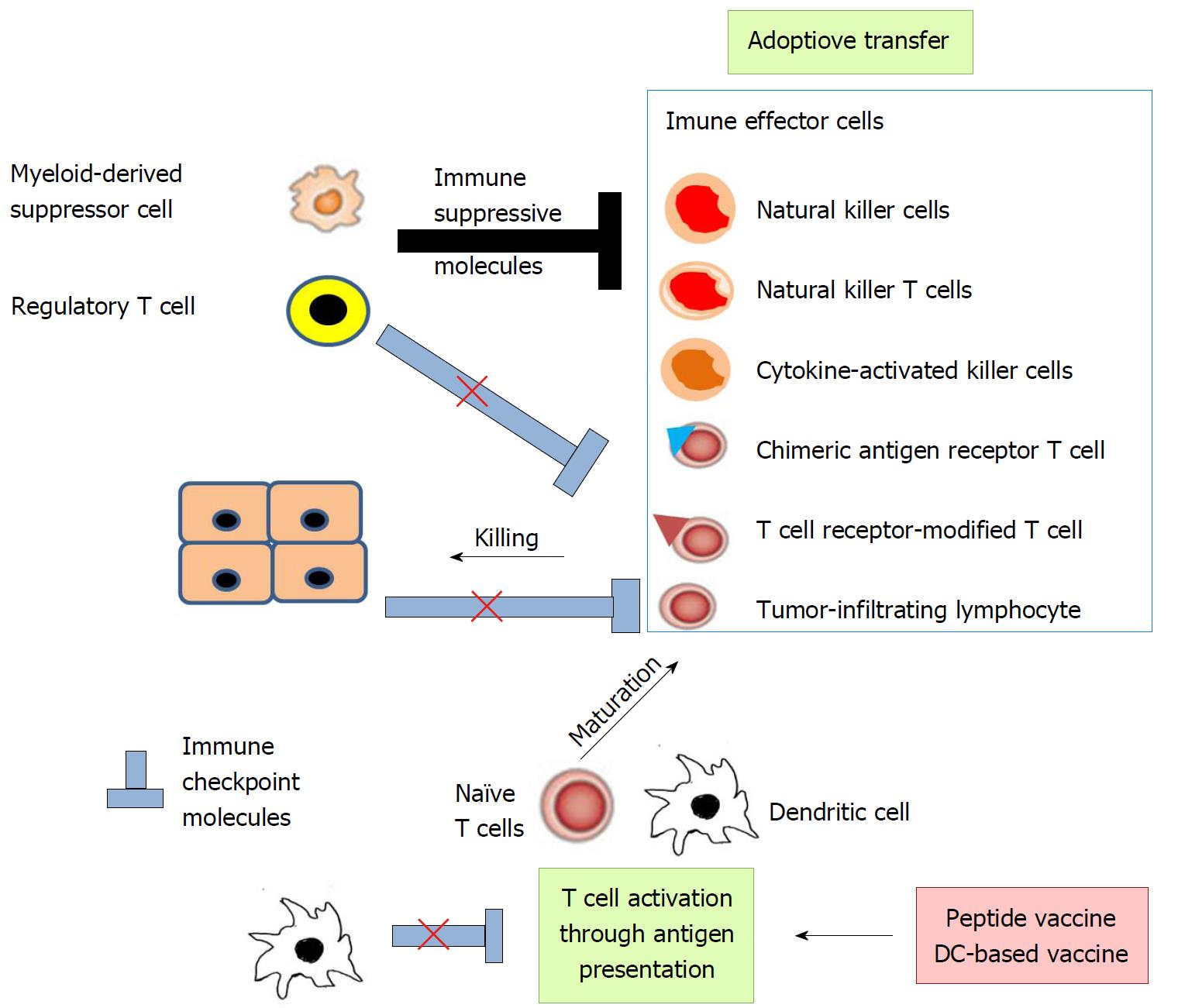
Figure 3 Strategies of immune therapy.
Immune therapy can be classified to two types, promotion of immune effector cell function and reversal of depressed anti-tumor immunity. Immune effector cell function can be enhanced by peptide vaccine, DC-based vaccine, and adoptive transfer of effector cells including tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), T cell receptor (TCR)-modified T cells, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, NKT cells, and cytokine-activated killer cells (CIKs). Depressed anti-tumor immunity can be reversed by the blockade of immune checkpoint pathways and immune suppressor cells including regulatory T cells (Tregs) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs).
- Citation: Mukaida N, Nakamoto Y. Emergence of immunotherapy as a novel way to treat hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(17): 1839-1858
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i17/1839.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i17.1839