Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2018; 24(16): 1779-1794
Published online Apr 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i16.1779
Published online Apr 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i16.1779
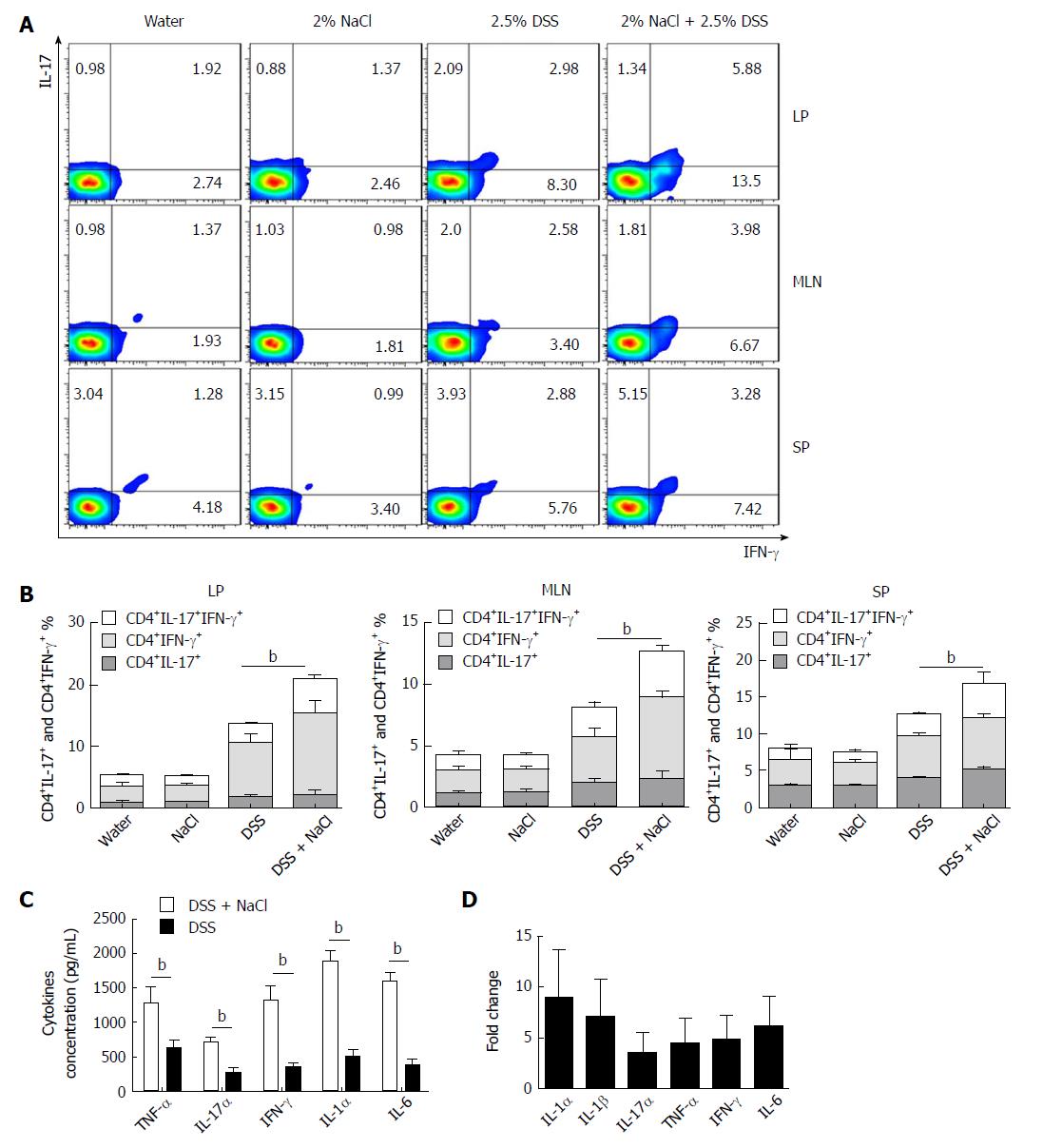
Figure 2 NaCl promotes CD4+IFN-γ+IL-17+ T cell increase and inflammatory cytokine secretion in DSS-treated mice.
A: The CD4+IFN-γ+IL-17+ T cells in LP, MLN and SP from mice treated with NaCl and/or DSS were detected by flow cytometry; B: Combined flow cytometry data of CD4+IL-17+, CD4+IFN-γ+ and CD4+IFN-γ+IL-17+ T cell subsets distribution in LP, MLN and SP; C: Colon tissues collected from mice treated with DSS or DSS + NaCl, which were washed with phosphate-buffered saline and cultured for 24 h, and the supernatants were collected and detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; D: Colon tissues collected from mice treated with NaCl and DSS (or only DSS) were detected by RT-PCR. The relative fold-change in DSS + NaCl-treated mice vs DSS-treated mice. In all the panels, data indicate three separate experiments, whereby 3 mice per group were used in each experiment. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; LP: Lamina propria; MLN: Mesenteric lymph node; SP: Spleen.
- Citation: Guo HX, Ye N, Yan P, Qiu MY, Zhang J, Shen ZG, He HY, Tian ZQ, Li HL, Li JT. Sodium chloride exacerbates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by tuning proinflammatory and antiinflammatory lamina propria mononuclear cells through p38/MAPK pathway in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(16): 1779-1794
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i16/1779.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i16.1779