Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2018; 24(16): 1748-1765
Published online Apr 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i16.1748
Published online Apr 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i16.1748
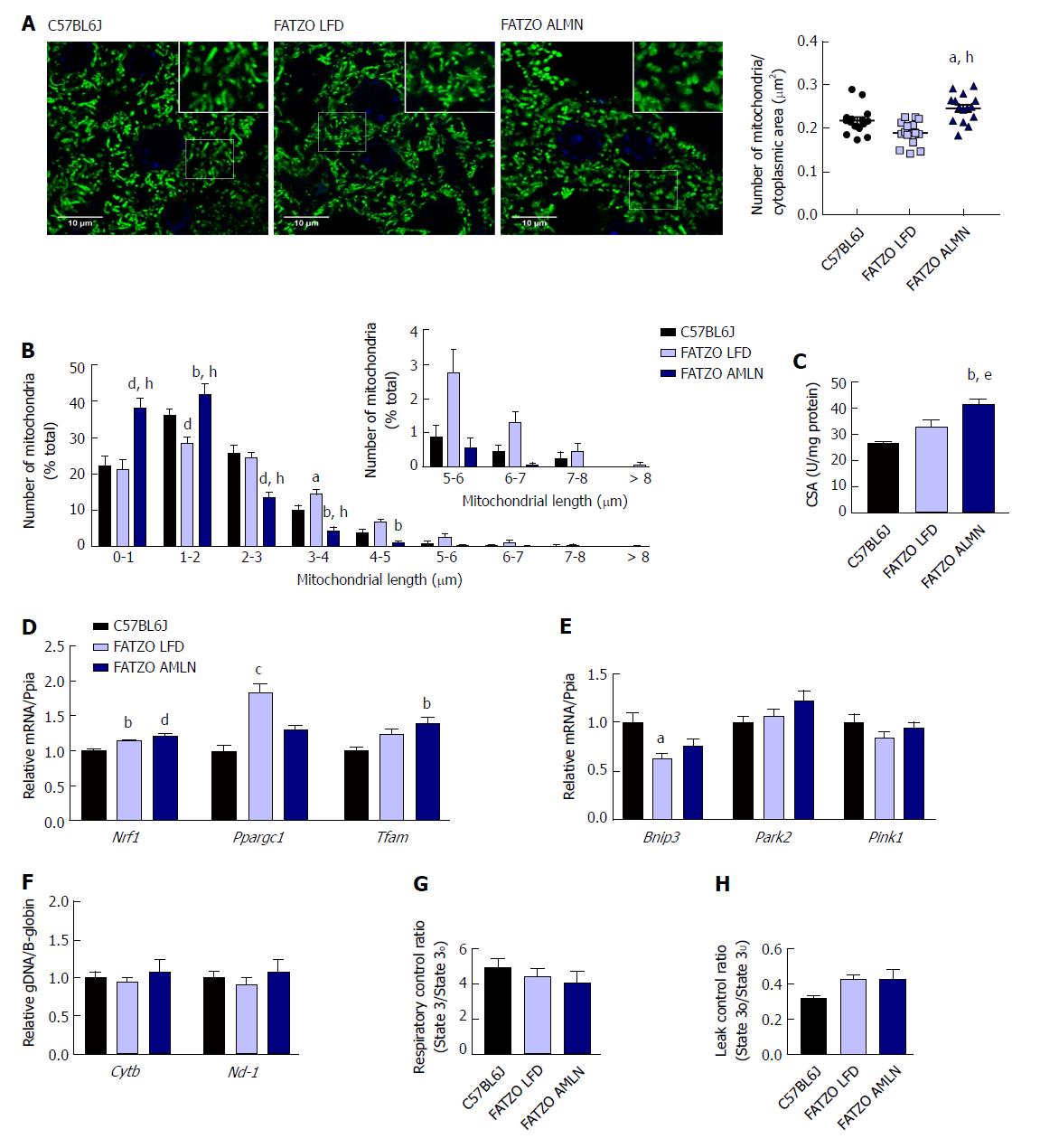
Figure 9 Mitochondrial content alterations in FATZO mice are associated with increased biogenesis and elevated proton leak.
(A): Confocal images of HSP60 stained liver sections with quantification of mitochondrial number per cytoplasmic area. Scale bar = 10 μm; (B): Histogram depicting the number of mitochondria per binned mitochondrial length as a percentage of total mitochondria per cell; (C): Mitochondrial content measured by citrate synthase activity of isolated hepatic mitochondria; (D): Expression of hepatic mitochondrial biogenesis genes; (E): Relative hepatic expression of mitophagy-associated genes; (F): Quantification of mitochondrial genome-encoded CytB or Nd1 relative to nuclear-encoded β- globin from total genomic DNA extracted from the liver; (G): Mitochondrial respiratory control ratio; (H): Mitochondrial leak control ratio. aP ≤ 0.05, bP ≤ 0.01, cP ≤ 0.001, dP ≤ 0.0001 vs C57BL6J; eP ≤ 0.05, hP ≤ 0.0001 vs LFD. LFD: Low-fat diet.
- Citation: Boland ML, Oldham S, Boland BB, Will S, Lapointe JM, Guionaud S, Rhodes CJ, Trevaskis JL. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis severity is defined by a failure in compensatory antioxidant capacity in the setting of mitochondrial dysfunction. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(16): 1748-1765
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i16/1748.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i16.1748