Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2018; 24(16): 1679-1707
Published online Apr 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i16.1679
Published online Apr 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i16.1679
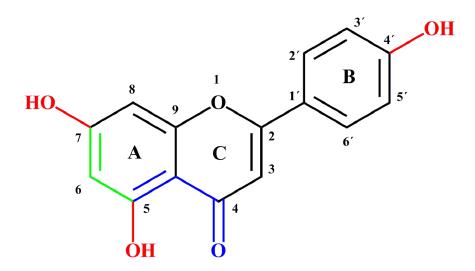
Figure 3 Naringenin antioxidant activity-structure relationship.
In red: Hydroxyl substituents (OH) that have high reactivity against reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species. In green: 5,7-m-dihydroxy arrangement in the A-ring serves to stabilize the structure after donating electrons to free radicals. In blue: The association between 5-OH and 4-oxo substituents contributes to the chelation of compounds such as heavy metals.
- Citation: Hernández-Aquino E, Muriel P. Beneficial effects of naringenin in liver diseases: Molecular mechanisms. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(16): 1679-1707
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i16/1679.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i16.1679