Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2018; 24(12): 1299-1311
Published online Mar 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i12.1299
Published online Mar 28, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i12.1299
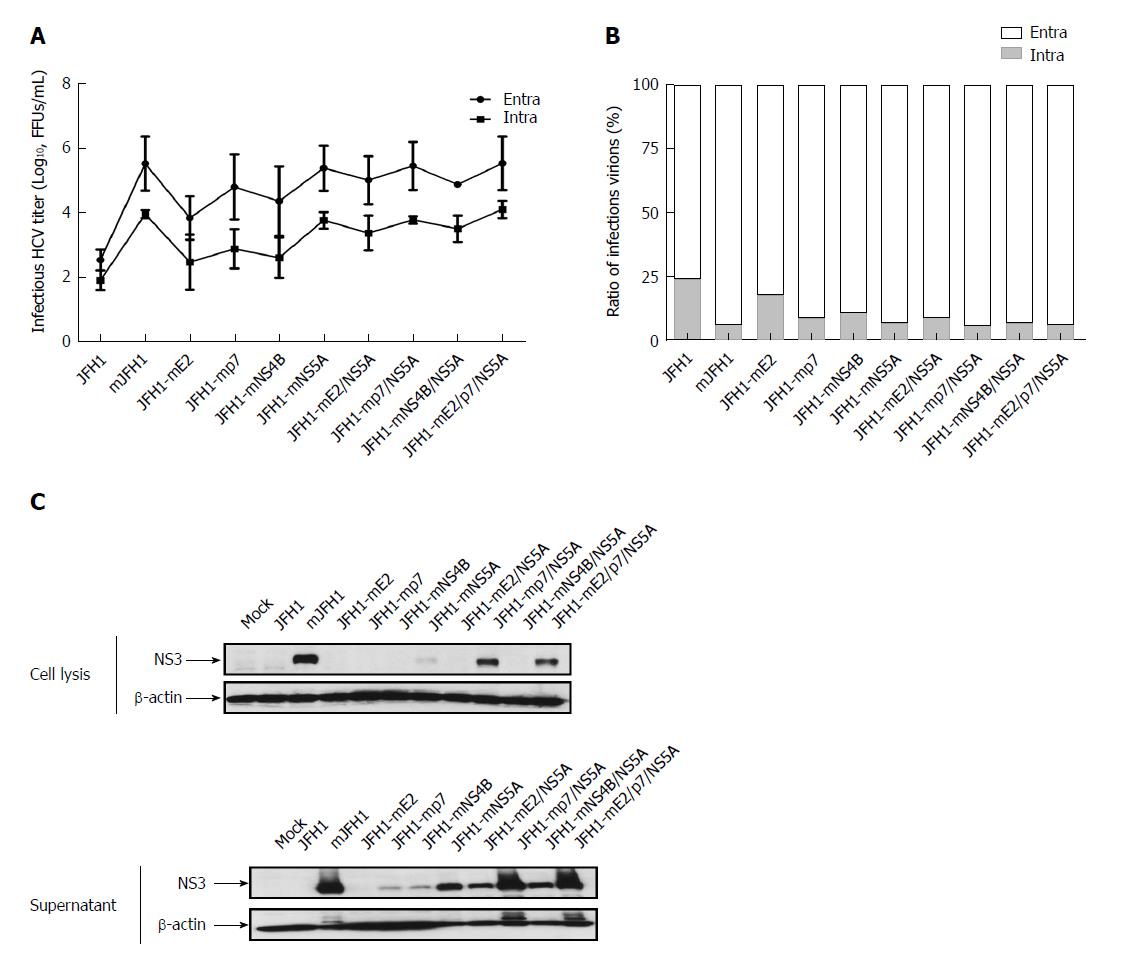
Figure 4 Effect of the adaptive mutations on the virion release.
A: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA was electroporated into Huh7.5 cells to produce the recombinants of adapted virus. At 72 h after transfection, the infectivity titers of the culture supernatants and cell lysates were measured. Viral titers are expressed as FFUs/mL. The data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3); B: HCV RNA was electroporated into Huh7.5 cells to produce the recombinants of adapted virus. At 72 h after transfection, the infectivity titers of the culture media and cell lysates were measured. The extracellular and intracellular viral titers were measured. The relative ratios of infectious virions are shown. The results were from three independent experiments; C: The naive Huh7.5 cells were infected with the culture media and cell lysates. At 72 h after infection, cells were lysed with RIPA buffer, and analyzed by Western blot.
- Citation: Wang Q, Li Y, Liu SA, Xie W, Cheng J. Cell culture-adaptive mutations in hepatitis C virus promote viral production by enhancing viral replication and release. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(12): 1299-1311
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i12/1299.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i12.1299