Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2017; 23(9): 1568-1575
Published online Mar 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i9.1568
Published online Mar 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i9.1568
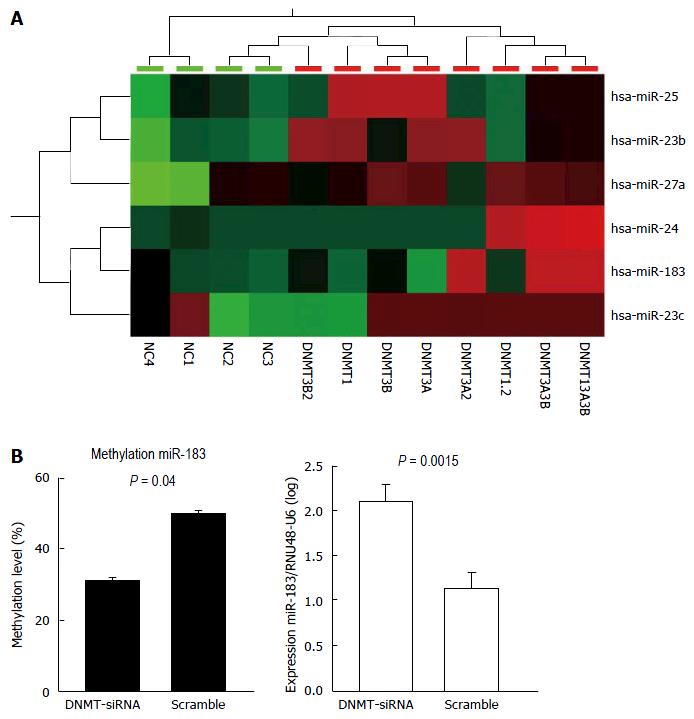
Figure 1 Upregulated microRNAs after DNA methyltransferases knockdown (A); and Methylation and expression changes of hsa-miR-183 after DNA methyltransferases knockdown (B).
A: Cluster analysis after single and combined DNMT knockdown using siRNAs (as indicated in the lower panel) shows upregulation of selected microRNAs (right panel). High, intermediate, and low microRNA expression levels in the heatmap are indicated with red, black, and green, respectively. B: Upon DNMT1 knockdown in HLE cell lines, DNA methylation at the promoter of miR-183 decreased significantly (right panel, P = 0.0015) accompanied by elevated miR-183 expression (left panel, P = 0.04). NC = negative control siRNA and DNMT (1, 3A, 3B) = DNA methyl transferase 1, -3A, -3B siRNA treated samples. DNMT: DNA methyltransferase.
- Citation: Anwar SL, Krech T, Hasemeier B, Schipper E, Schweitzer N, Vogel A, Kreipe H, Buurman R, Skawran B, Lehmann U. hsa-mir-183 is frequently methylated and related to poor survival in human hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(9): 1568-1575
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i9/1568.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i9.1568