Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2017; 23(7): 1203-1214
Published online Feb 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i7.1203
Published online Feb 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i7.1203
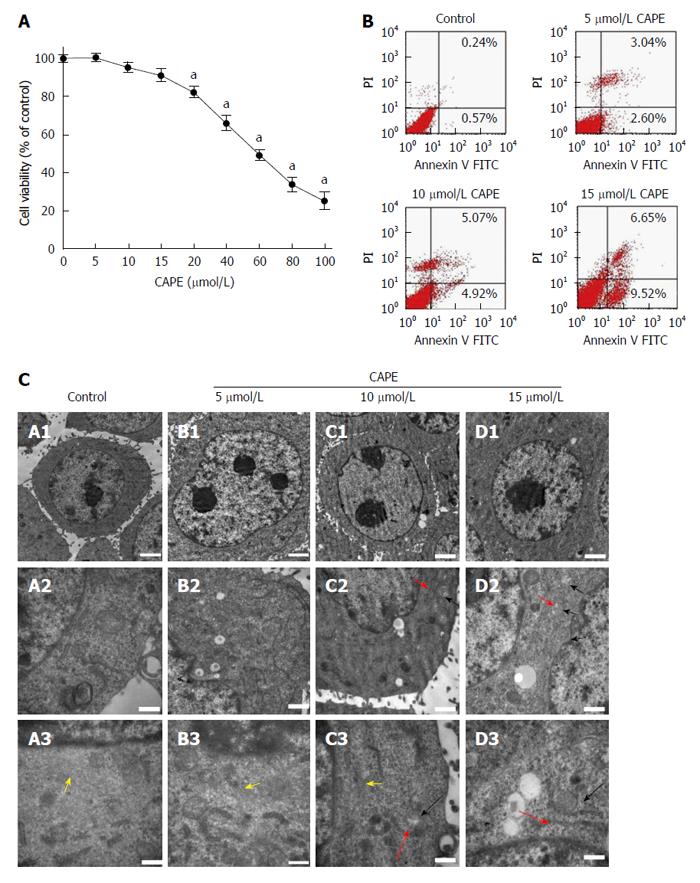
Figure 1 Effect of different concentrations of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on biological characteristics of hepatic stellate cell-T6 cells.
After HSC-T6 cells were treated with CAPE(0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 40, 60, 80 and 100 μmol/L) for 24 h (A) the effect of CAPE on the viability of HSC-6 cells was detected by the MTT assay; B: Cell apoptosis was investigated using annexin V-FITC and PI and the proportion of cell apoptosis increased in a concentration-dependent manner; C: Ultrastructure of the HSC-T6 cells. The normal structure is shown in the control groups (group A). The treatment groups (groups B, C, and D) displayed prominent myofilament disarray and rupture, cytoplasmic vacuolization, and significant mitochondrial swelling (black bar: mitochondria; red bar: Endoplasmic reticulum; yellow bar: myofilament). The upper scale bar = 2 μm, the middle scale bar = 1 μm, and the lower scale bar = 0.5 μm. The data represent averages of the results of four independent experiments. aP < 0.05 vs control. CAPE: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester.
- Citation: Yang N, Shi JJ, Wu FP, Li M, Zhang X, Li YP, Zhai S, Jia XL, Dang SS. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester up-regulates antioxidant levels in hepatic stellate cell line T6 via an Nrf2-mediated mitogen activated protein kinases pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(7): 1203-1214
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i7/1203.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i7.1203