Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2017; 23(6): 986-998
Published online Feb 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.986
Published online Feb 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.986
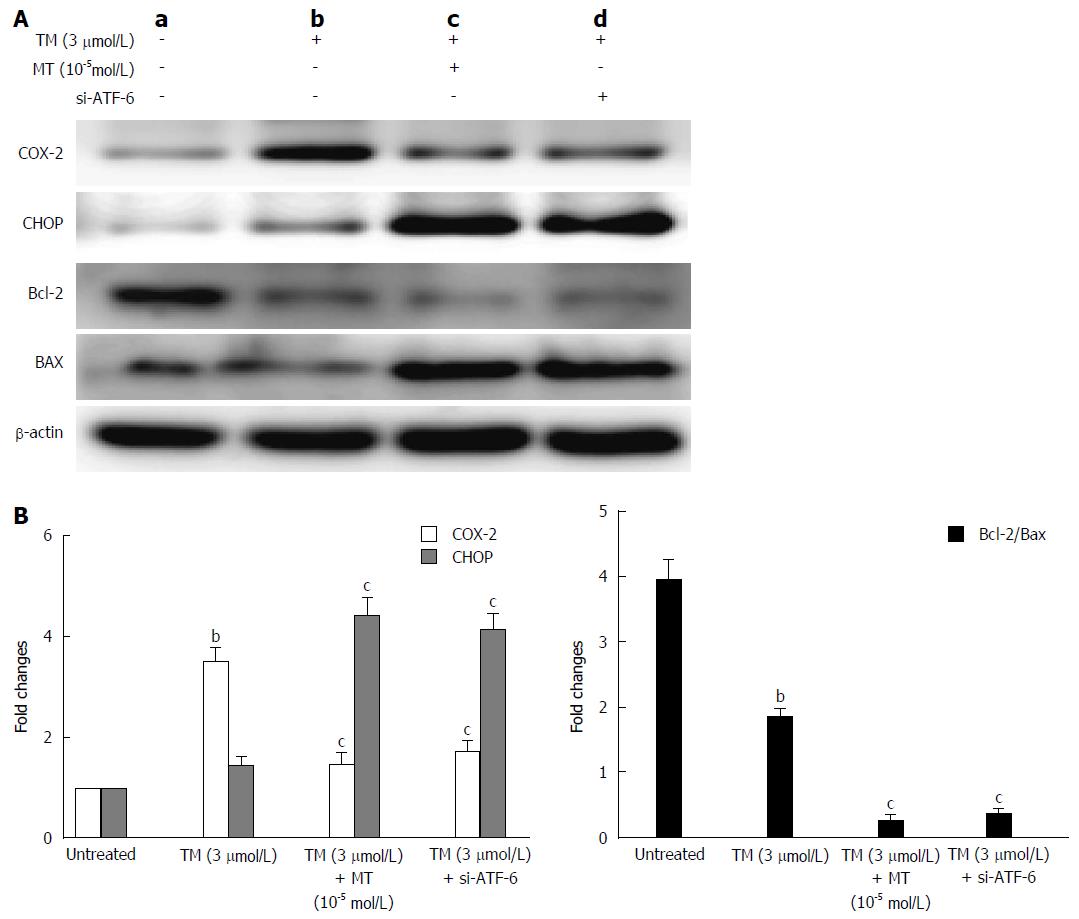
Figure 7 Pathway by which melatonin sensitized HepG2 to endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis.
A: a, Untreated HepG2 cells; b, HepG2 cells treated by tunicamycin (TM) only; c, HepG2 cells treated by TM, melatonin (10-5 mmol/L); d: HepG2 cells treated by TM and ATF-6 siRNA. Equal protein amounts of cell lysates were subjected to western blot assay using anti-COX-2, anti-CHOP, anti-Bcl-2, and anti-Bax. β-actin in the same HepG2 cell extract was used as an internal reference; B: Optical density reading values of specific proteins are represented as fold-differences relative to the loading control protein, β-actin. cP < 0.01, CHOP vs the Bcl-2 and Bax expression, bP < 0.01, vs the untreated HepG2 cells. ATF-6: Activating transcription factor 6; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; CHOP: CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein homologous protein; MT: Melatonin.
- Citation: Bu LJ, Yu HQ, Fan LL, Li XQ, Wang F, Liu JT, Zhong F, Zhang CJ, Wei W, Wang H, Sun GP. Melatonin, a novel selective ATF-6 inhibitor, induces human hepatoma cell apoptosis through COX-2 downregulation. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(6): 986-998
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i6/986.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.986