Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2017; 23(6): 976-985
Published online Feb 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.976
Published online Feb 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.976
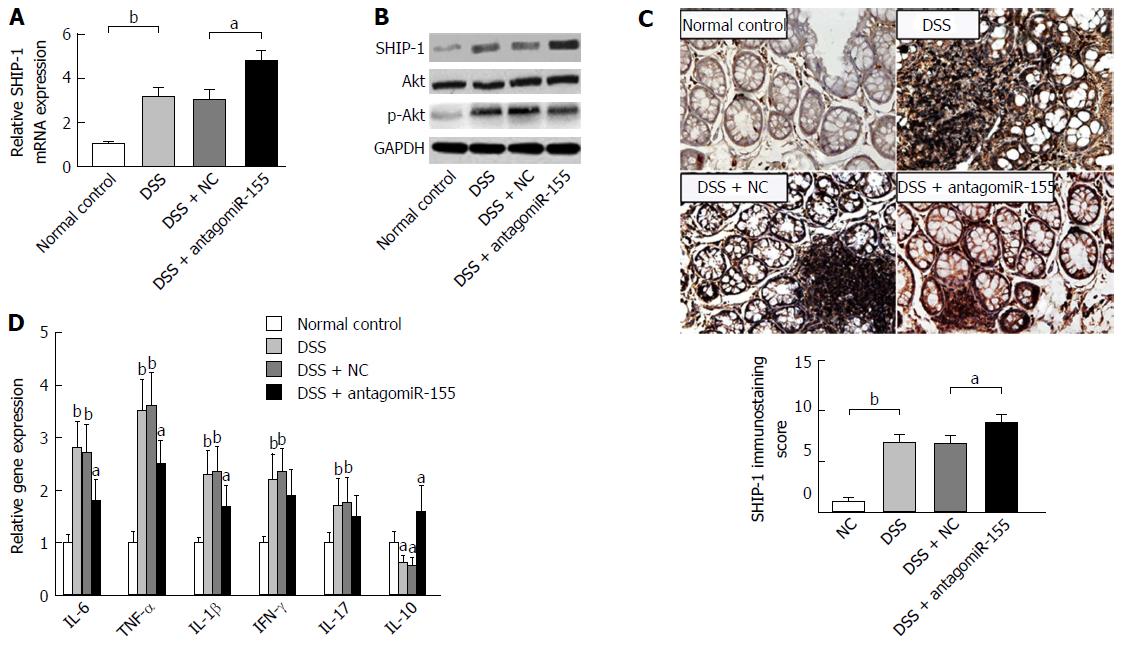
Figure 5 Inhibition of microRNA-155 alleviates colitis by regulating the SHIP-1/Akt signaling pathway.
A: AntagomiR-155 treatment elevated the mRNA expression of SHIP-1. bP < 0.01, DSS vs control; aP < 0.05, DSS + antagomiR-155 vs DSS + NC; B: Western blot analysis of the protein levels of SHIP-1, Akt, and p-Akt after antagomiR-155 treatment, with normalized to GAPDH; C: Immunohistochemistry staining and semi-quantification for SHIP-1 in mice colon tissues. bP < 0.01, DSS vs control; aP < 0.05, DSS + antagomiR-155 vs DSS + NC. D: The mRNA expression levels of key factors involved in colitis-related inflammatory response. Comparison was conducted between groups: DSS, DSS + NC vs control; and DSS + antagomiR-155 vs DSS, DSS + NC. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium.
- Citation: Lu ZJ, Wu JJ, Jiang WL, Xiao JH, Tao KZ, Ma L, Zheng P, Wan R, Wang XP. MicroRNA-155 promotes the pathogenesis of experimental colitis by repressing SHIP-1 expression. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(6): 976-985
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i6/976.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.976