Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2017; 23(6): 964-975
Published online Feb 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.964
Published online Feb 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.964
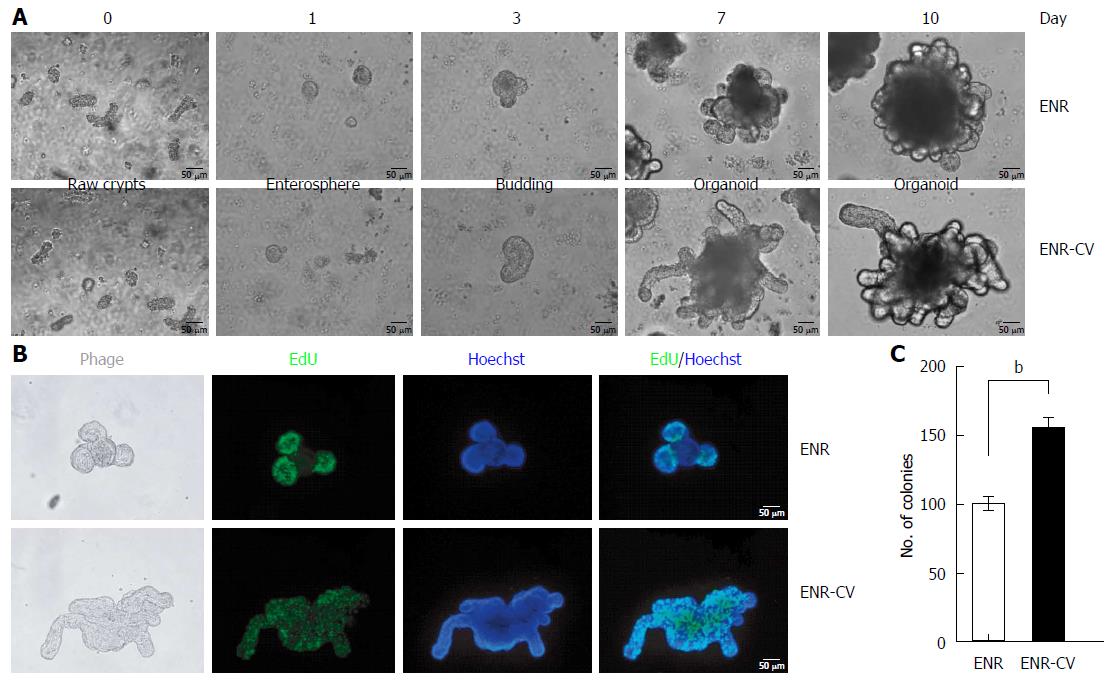
Figure 1 Establishment of small intestinal organoid culture under epidermal growth factor/noggin/r-spondin1 and epidermal growth factor/noggin/r-spondin1-/CHIR99021/VPA conditions.
Crypts were isolated from the small intestines of C57/B6 mice at ages 9-12 wk and were resuspended in growth factor-reduced Matrigel. A: Time course of the growth of isolated crypts at passage 0 (P0) under two different culture media. Enterospheres formed on day 1, budding appeared on day 3, and robust budding was observed on days 5-10. Scale bars: 50 μm. B: Organoids were incubated with the thymidine analog EdU (green) for 1 h, and freshly isolated crypts were cultured for 6 d. Images were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy, and nuclei were double stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bars: 50 μm. C: Numbers of organoids grown in two different media for 7 d. Organoids exhibiting at least two budding structures in each group were counted. The data are shown as means ± SDs of triplicate experiments (bP < 0.01, Student’s t-tests).
- Citation: Han SH, Shim S, Kim MJ, Shin HY, Jang WS, Lee SJ, Jin YW, Lee SS, Lee SB, Park S. Long-term culture-induced phenotypic difference and efficient cryopreservation of small intestinal organoids by treatment timing of Rho kinase inhibitor. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(6): 964-975
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i6/964.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i6.964