Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2017; 23(5): 817-829
Published online Feb 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i5.817
Published online Feb 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i5.817
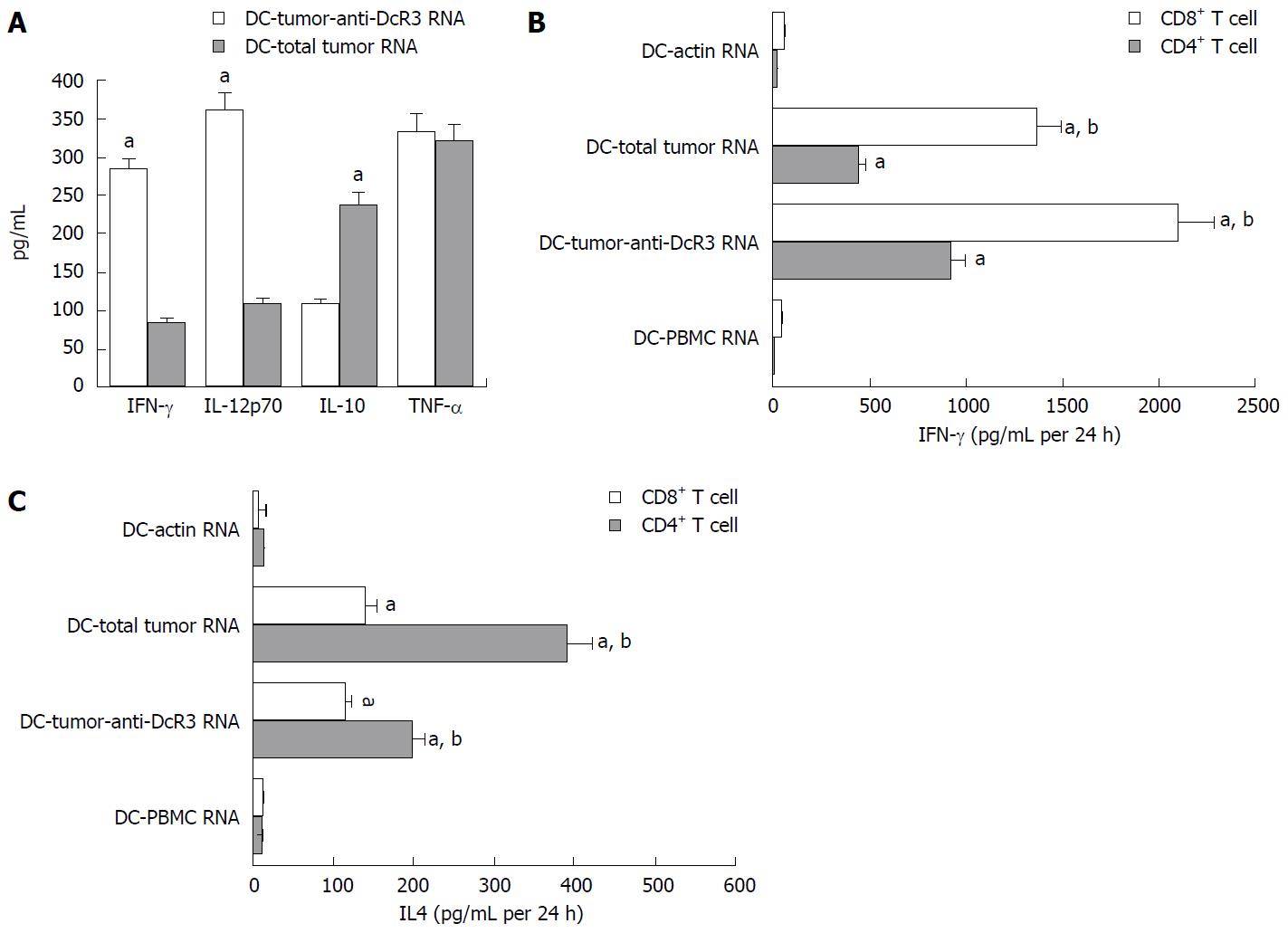
Figure 5 T cell responses induced by anti-DcR3 monoclonal antibody secreting dendritic cells.
The T cells were co-cultured with RNA-dendritic cells (DCs) for 24 h. Then, the supernatants were collected, and the cytokine levels were measured by ELISA assay. A: ELISA test showed the cytokines of IL-12p70 and IFN-γ secreted by T cells pulsed by DC-tumor-anti-DcR3 RNA were higher than those secreted by T cells pulsed by DC-total tumor RNA without significant change of TNF-α. Meanwhile, IL-10 level was lower in DC-tumor-anti-DcR3 RNA than in DC-total tumor RNA (aP < 0.05); B: CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells incubated with DCs encoding whole tumor antigens could produce extremely higher IFN-γ levels compared with those incubated with DCs as control or DCs treated with normal tissues (aP < 0.01). Furthermore, the CD4+ T and CD8+ T cells incubated with DCs co-transfected total tumor RNA and anti-DcR3 mAb mRNA produced higher IFN-γ levels than those incubated with DC-total tumor RNA (bP < 0.01); C: The CD4+ T and CD8+ T cells incubated with DCs loaded with whole tumor antigens showed a positive expression of IL-4, whereas a negative or weak expression of IL-4 was observed in DC-actin RNA and DC-PBMC RNA cells (aP < 0.01). Moreover, decreased levels of IL-4 production were detected in CD4+ T cells stimulated by DCs co-transfected with total tumor RNA and anti-DcR3 mAb mRNA compared with DCs transfected with total tumor RNA individually (bP < 0.01). The experiment was repeated three times representatively, and results are shown as mean ± SD. IL: Interleukin; ELISA: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; PBMC: Peripheral blood monocyte cell; mAb: Monoclonal antibody.
- Citation: Chen J, Guo XZ, Li HY, Zhao JJ, Xu WD. Dendritic cells engineered to secrete anti-DcR3 antibody augment cytotoxic T lymphocyte response against pancreatic cancer in vitro. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(5): 817-829
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i5/817.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i5.817