Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2017; 23(5): 743-750
Published online Feb 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i5.743
Published online Feb 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i5.743
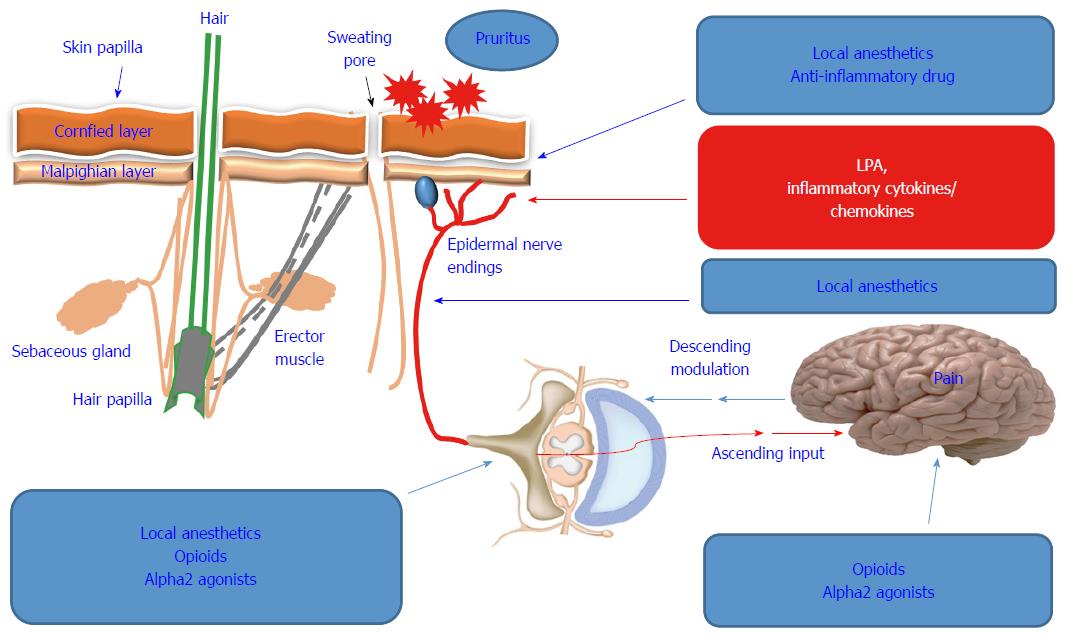
Figure 2 Overview of the treatment options of hepatitis C virus-associated pruritus.
Once the underlying factors [elevated concentration of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines] causing pruritus have been determined, the treatment strategy can be based on the reduction of the pain or neutralization of the elevated concentration of LPA, pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines using local anesthetics, anti-inflammatory drug, Opioids or alpha2 agonists.
- Citation: Alhmada Y, Selimovic D, Murad F, Hassan SL, Haikel Y, Megahed M, Hannig M, Hassan M. Hepatitis C virus-associated pruritus: Etiopathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(5): 743-750
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i5/743.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i5.743