Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2017; 23(48): 8500-8511
Published online Dec 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i48.8500
Published online Dec 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i48.8500
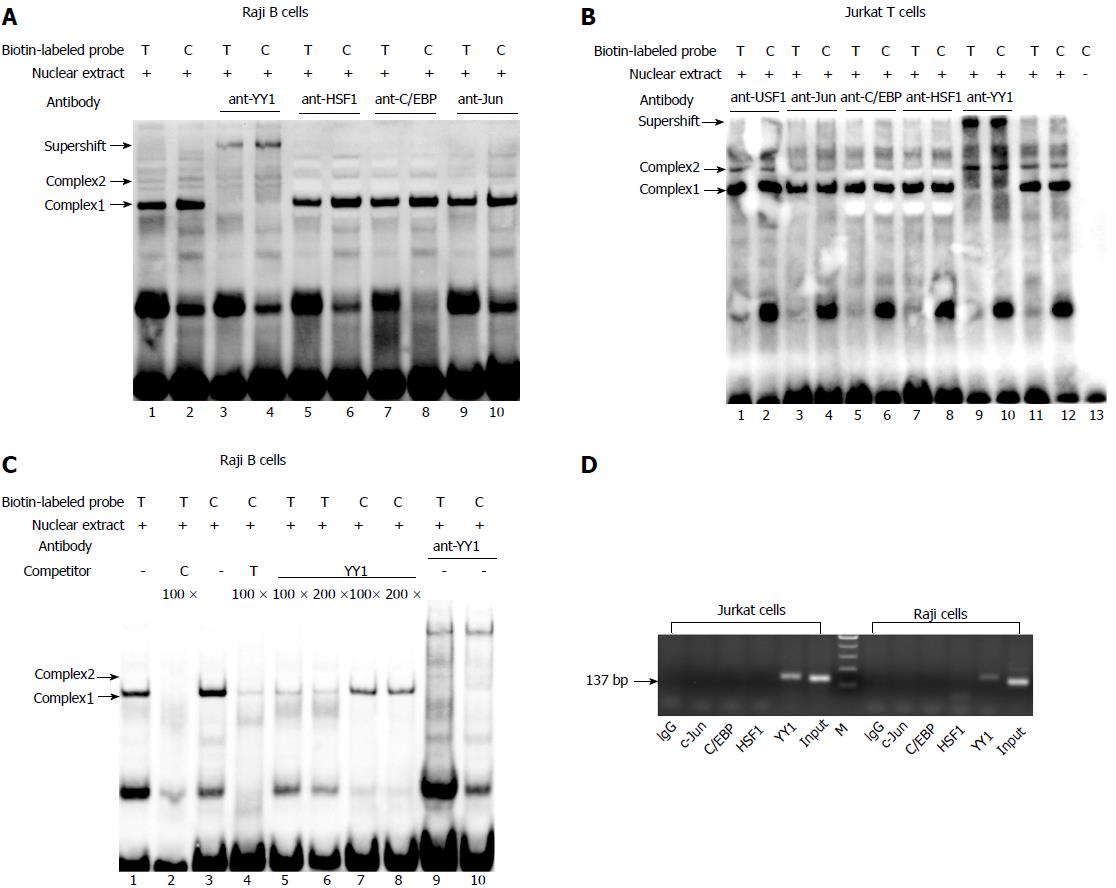
Figure 1 Identification of transcription factor binding to the T-1993C SNP site of TBX21 promoter in vitro and in vivo.
A, B: EMSA analysis with biotin-labeled probes carrying the -1993T and -1993C allele and with nuclear extract from Jurkat cells and Raji cells was performed in the presence of anti-YY1 antibody; C: EMSA with biotin-labeled probes and with nuclear extract from Raji cells was performed in the presence of 100-200-fold excess of unlabeled self-oligonucleotide or YY1 probe; D: In vivo binding of YY1 to the T-1993C SNP site of the TBX21 promoter. ChIP assays with an anti-YY1, anti-C/EBPβ, ant-C-Jun, or control antibody (rabbit IgG) were performed on Jurkat cells or Raji cells. Input DNA or Immunoprecipitated DNA was used as template for PCR amplification of a 137-bp amplicon encompassing TBX21-1993. EMSA: Electrophoretic mobility shift assay; ChIP: Chromatin immunoprecipitation.
- Citation: Sun W, Wu HY, Chen S. Influence of TBX21 T-1993C variant on autoimmune hepatitis development by Yin-Yang 1 binding. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(48): 8500-8511
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i48/8500.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i48.8500