Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2017; 23(47): 8415-8425
Published online Dec 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i47.8415
Published online Dec 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i47.8415
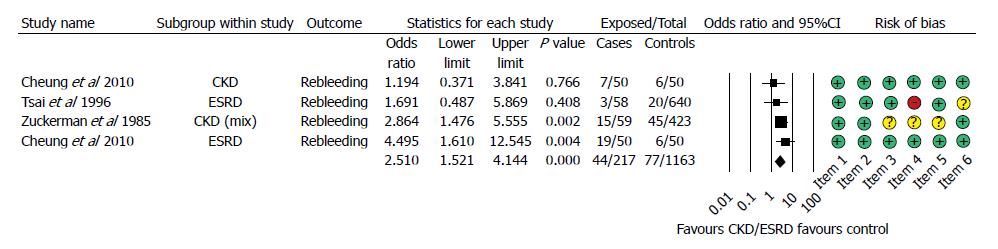
Figure 4 Forest plot representing the rebleeding rate in gastrointestinal bleeding patients with normal and impaired renal function.
Size of squares for risk ratio reflects weight of trial in pooled analysis. Horizontal bars represent 95%CI. CKD: Chronic kidney disease; ESRD: End-stage renal disease.
- Citation: Hágendorn R, Farkas N, Vincze Á, Gyöngyi Z, Csupor D, Bajor J, Erőss B, Csécsei P, Vasas A, Szakács Z, Szapáry L, Hegyi P, Mikó A. Chronic kidney disease severely deteriorates the outcome of gastrointestinal bleeding: A meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(47): 8415-8425
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i47/8415.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i47.8415