Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2017; 23(46): 8248-8255
Published online Dec 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8248
Published online Dec 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8248
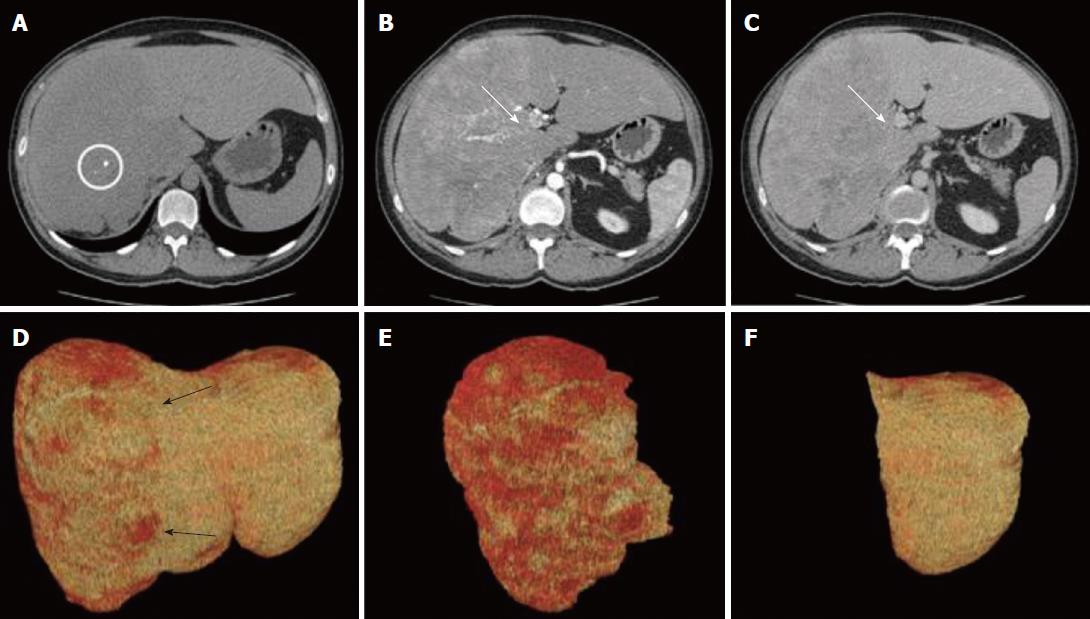
Figure 1 Computer tomography examination and virtual resection.
A: Pre-contrast acquisition, axial image cranial to the hilar plane showing a large, hypo-attenuating lobulated lesion involving the right hemi-liver and part of the segment 4 (white circle: calcification within the neoplastic lesion); B and C: Axial images across the hilar plane during arterial (B) and portal (C) phase. Then neoplastic, lobulated lesion shows early arterial enhancement resulting in hypo-attenuation during the portal phase. The right portal branch is not visible due to neoplastic infiltration (white arrows); D-F: Virtual resection, volume renderings of CT images; D: Total liver volume; the non-homogenous red color of the right hemi-liver corresponds to the lesion (black arrows); E: Tumor lesion; F: Future remnant liver corresponding to segments 2 and 3.
- Citation: Meletani T, Cantini L, Lanese A, Nicolini D, Cimadamore A, Agostini A, Ricci G, Antognoli S, Mandolesi A, Guido M, Alaggio R, Giuseppetti GM, Scarpelli M, Vivarelli M, Berardi R. Are liver nested stromal epithelial tumors always low aggressive? World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(46): 8248-8255
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i46/8248.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8248