Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2017; 23(46): 8152-8168
Published online Dec 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8152
Published online Dec 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8152
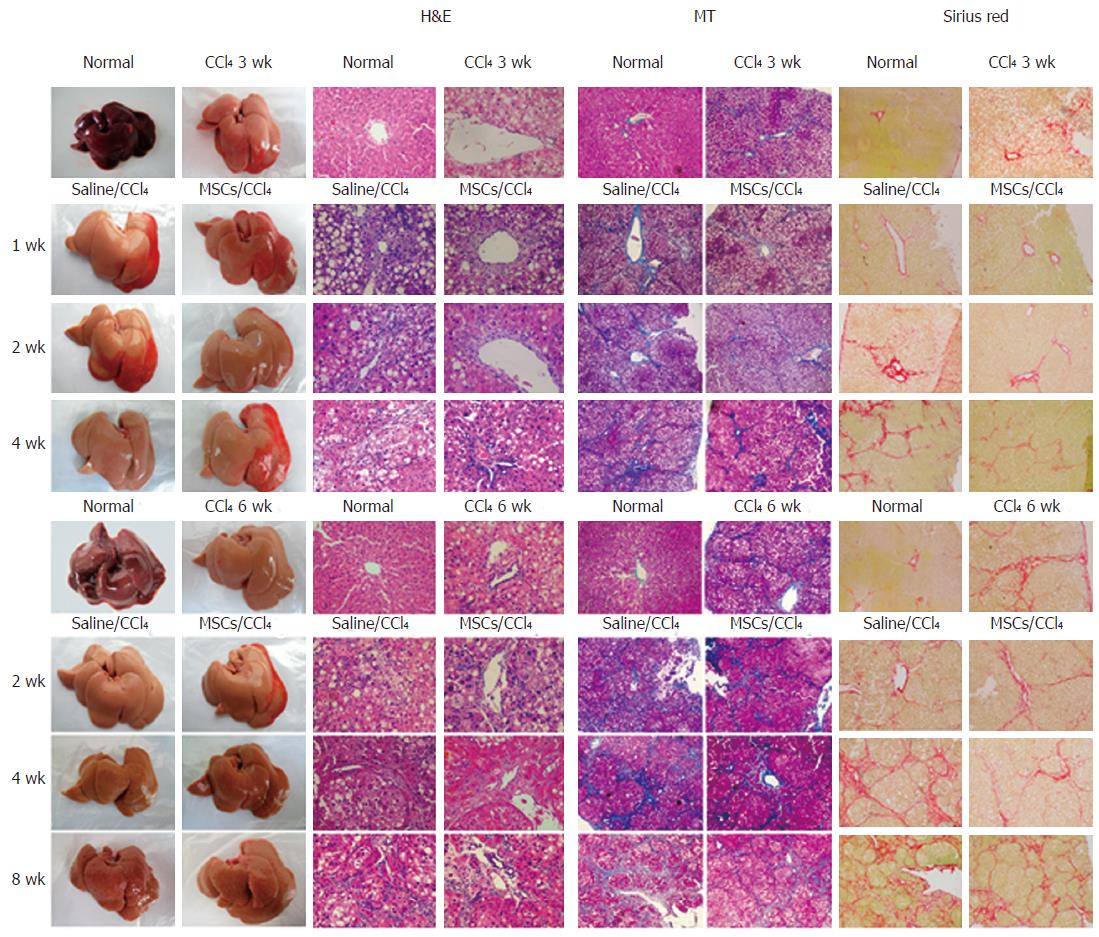
Figure 4 Representative photographs of the fresh livers, hematoxylin and eosin staining (H&E staining), Masson's trichrome staining (MT staining) and sirius red staining in rat fibrotic or cirrhotic hepatic tissues.
Liver sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E, ×400), Masson's trichrome (MT, ×100) and Sirius red (×100) or representative photographs of the fresh livers without fixation were used to evaluate histopathological changes for liver tissues in control conditions; with CCl4 for 3 wk; or with 1, 2, and 4 wk in fibrotic rat tissues; with CCl4 for 6 wk; or with 2, 4, and 8 wk in cirrhotic rat tissues after human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell (hUC-MSC) or saline injection into rats.
- Citation: Zhang GZ, Sun HC, Zheng LB, Guo JB, Zhang XL. In vivo hepatic differentiation potential of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Therapeutic effect on liver fibrosis/cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(46): 8152-8168
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i46/8152.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8152