Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2017; 23(46): 8152-8168
Published online Dec 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8152
Published online Dec 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8152
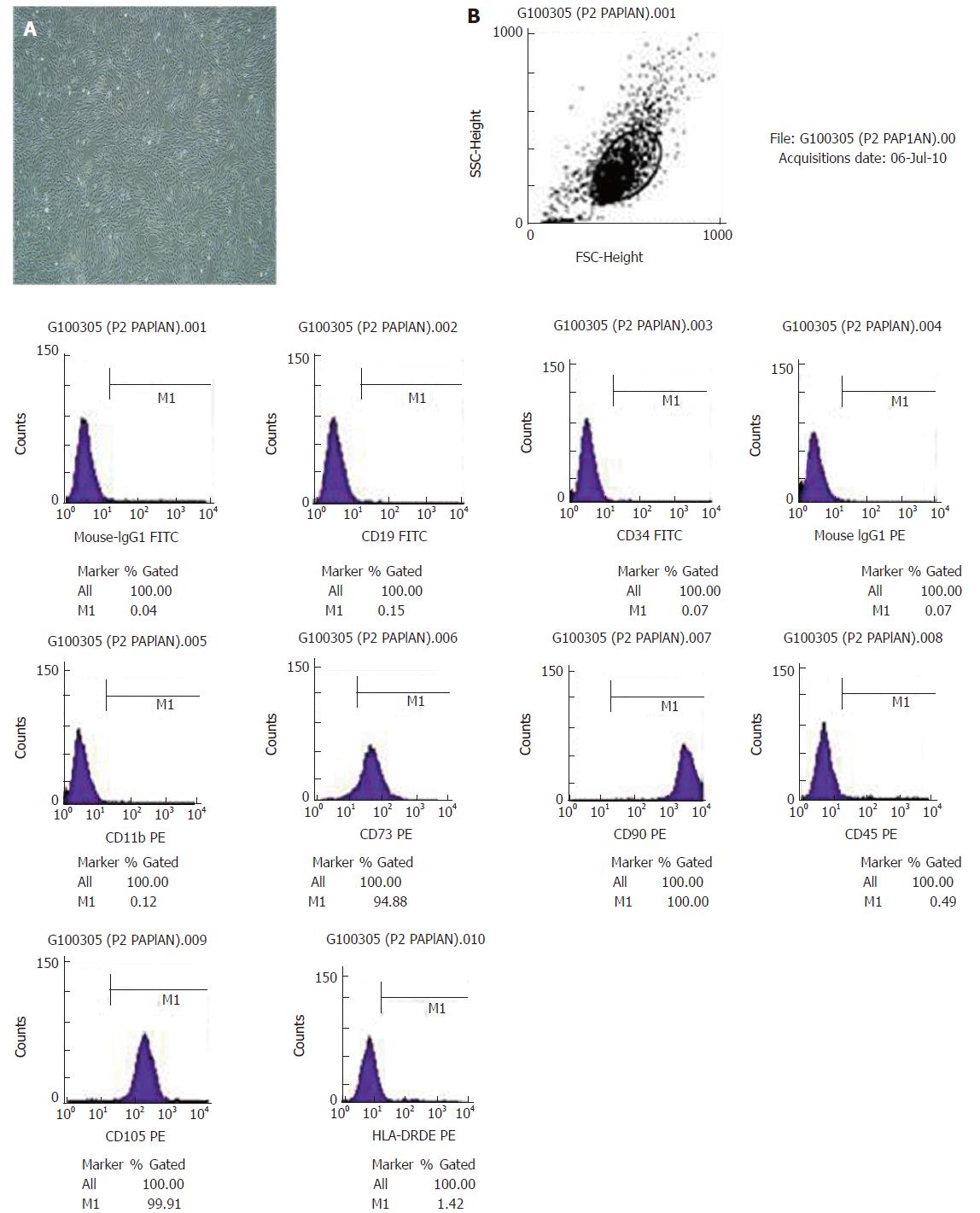
Figure 1 Morphology of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells and immunophenotype analysis using FACS.
A: The morphology of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) (× 100); B: Immunophenotype analysis using FACS. The 3rd passage hUC-MSCs are shown, and the adherent cells displayed a fibroblastic morphology. Immunophenotype analysis using FACS showed that hUC-MSCs were positive for the human MSC-specific markers CD90, CD105 and CD73 but were negative for CD34, CD19, CD11b, HLA-DR and CD45.
- Citation: Zhang GZ, Sun HC, Zheng LB, Guo JB, Zhang XL. In vivo hepatic differentiation potential of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Therapeutic effect on liver fibrosis/cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(46): 8152-8168
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i46/8152.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8152