Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2017; 23(46): 8120-8127
Published online Dec 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8120
Published online Dec 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8120
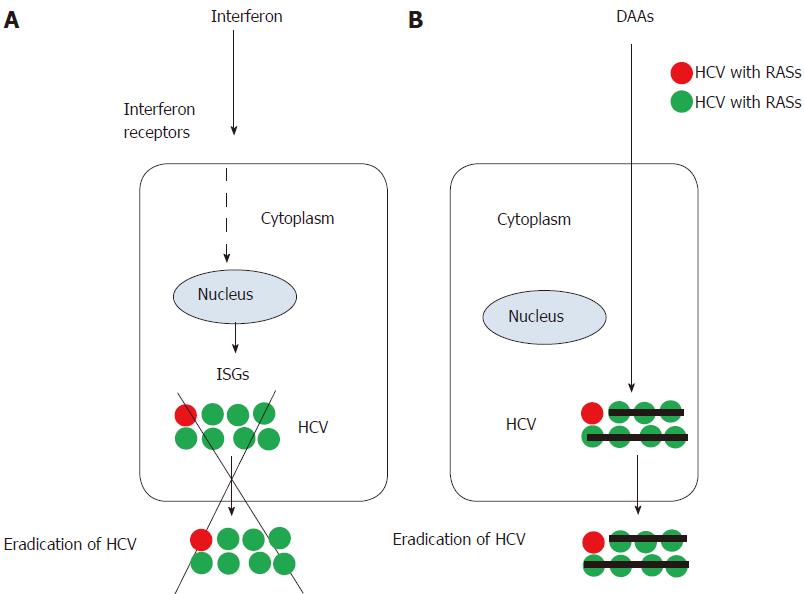
Figure 1 Eradication of hepatitis C virus by interferon and direct-acting antiviral agents against hepatitis C virus.
A: Interferon. Interferon induces interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) transcription after binding its receptors and antiviral proteins. ISGs eradicate hepatitis C virus (HCV) with or without resistance associated substitutions (RASs) although interleukin-28B (IL28B) genotypes have an effect on its treatment results. B: direct-acting antiviral agents (DAAs) easily eradicate HCV without RASs because DAAs work in HCV sequence-specific manner. In some cases, it is difficult for DAAs to eradicate HCV with RASs.
- Citation: Kanda T, Nirei K, Matsumoto N, Higuchi T, Nakamura H, Yamagami H, Matsuoka S, Moriyama M. Retreatment of patients with treatment failure of direct-acting antivirals: Focus on hepatitis C virus genotype 1b. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(46): 8120-8127
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i46/8120.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8120