Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2017; 23(46): 8109-8119
Published online Dec 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8109
Published online Dec 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8109
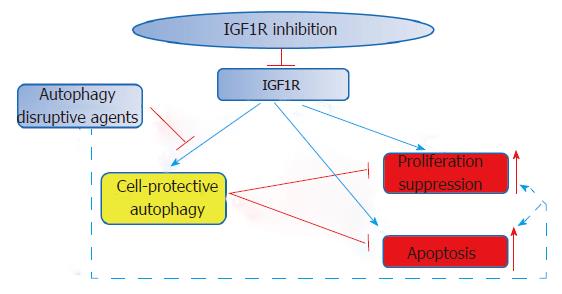
Figure 3 Proposed model for the bi-directional IGF1R signaling-dependent modulation of the autophagic pathway.
IGF1R targeting via suppression of the "canonical" PI3K/Akt/mTORC1 pathway stimulates the autophagy process. However, it can also result in a reduced formation of autophagosomal precursors at the plasma membrane. IGF1R depletion inhibits mTORC2, which reduces the activity of protein kinase C alpha and beta. This finally negatively impacts autophagosome precursor formation. IGF1R: Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; AKT: Serine/threonine kinase, named protein kinase B (PKB); mTORC1/2: Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1/2; PKC: Protein kinase C; ATG16L1: Autophagy-related protein 16-1.
- Citation: Sipos F, Székely H, Kis ID, Tulassay Z, Műzes G. Relation of the IGF/IGF1R system to autophagy in colitis and colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(46): 8109-8119
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i46/8109.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i46.8109