Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2017; 23(45): 8097-8103
Published online Dec 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i45.8097
Published online Dec 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i45.8097
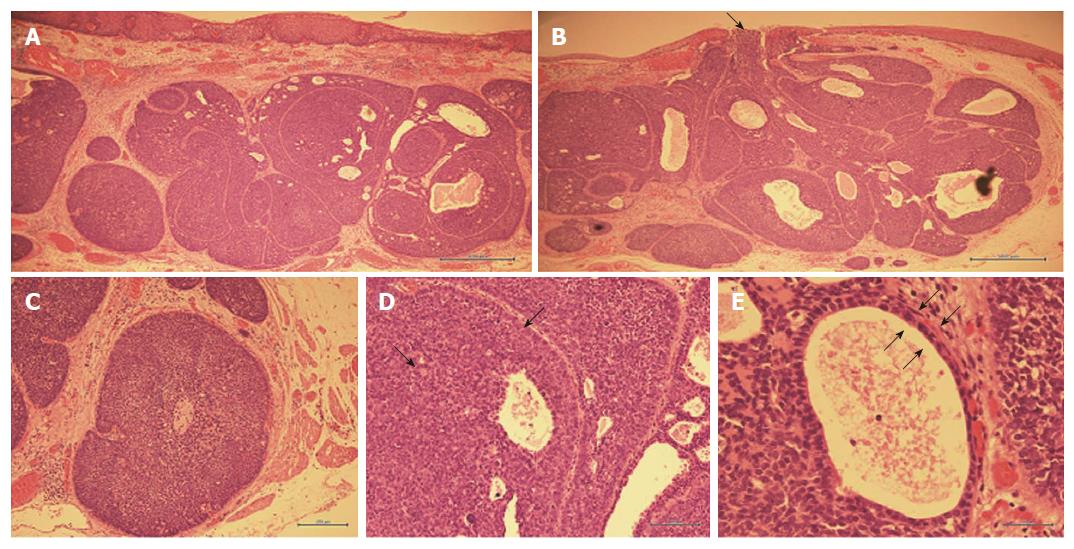
Figure 4 Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the resected specimen.
A: Main locus of submucosal tumor (× 40); B: Tumor protrusion into esophageal lumen (black arrows, × 40); C: Cribriform structure of tumor cells (× 100); D: Heterotypic cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm (black arrows, × 200); E: Bi-layered structure of tumor duct cells (black arrows, × 400).
- Citation: Yoshikawa K, Kinoshita A, Hirose Y, Shibata K, Akasu T, Hagiwara N, Yokota T, Imai N, Iwaku A, Kobayashi G, Kobayashi H, Fushiya N, Kijima H, Koike K, Kaneyama H, Ikeda K, Saruta M. Endoscopic submucosal dissection in a patient with esophageal adenoid cystic carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(45): 8097-8103
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i45/8097.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i45.8097