Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2017; 23(44): 7830-7839
Published online Nov 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i44.7830
Published online Nov 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i44.7830
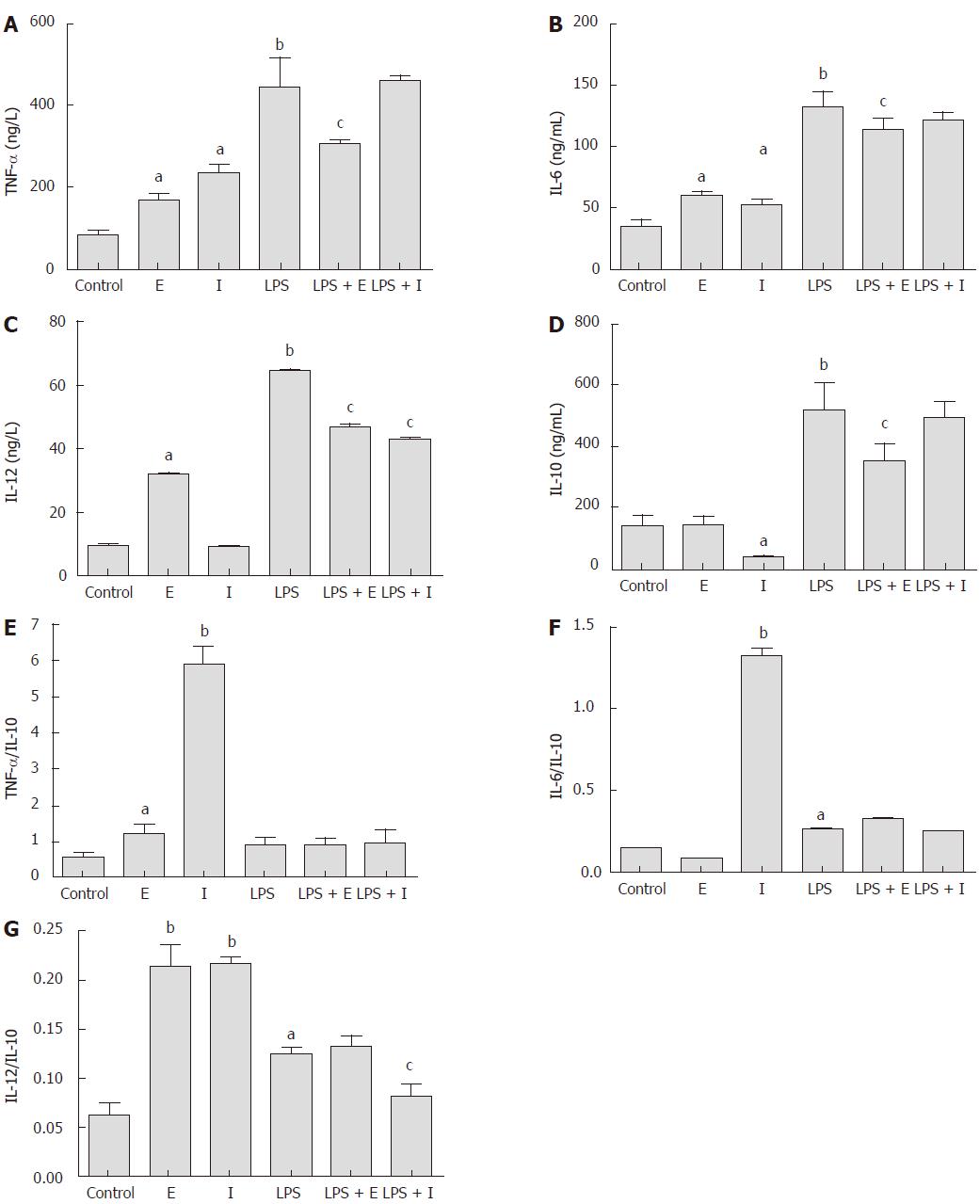
Figure 4 Effect of iDNA and eDNA on cytokine production by Raw267.
4 cells, including TNF-α (A), IL6 (B), IL-12 (C), IL-10 (D), and ratio of TNF-α (E), IL6 (F) and IL-12 (G) to IL-10. Cells were treated for 12 h with medium, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (1 μg/mL), eDNA (1 ng/mL), iDNA (1 ng/mL), eDNA(1 ng/mL) + LPS (1 μg/mL), or iDNA (1 ng/mL) + LPS (1 μg/mL) for 12 h. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 6). aP < 0.05, Significant differences between control and treatment; bP < 0.01, significant differences between control and treatment; cP < 0.05, significant differences between LPS treatment and treatment. E: Extracellular bacterial DNA; I: Intracellular bacterial DNA; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide.
- Citation: Qi C, Li Y, Yu RQ, Zhou SL, Wang XG, Le GW, Jin QZ, Xiao H, Sun J. Composition and immuno-stimulatory properties of extracellular DNA from mouse gut flora. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(44): 7830-7839
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i44/7830.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i44.7830