Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2017; 23(43): 7765-7775
Published online Nov 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i43.7765
Published online Nov 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i43.7765
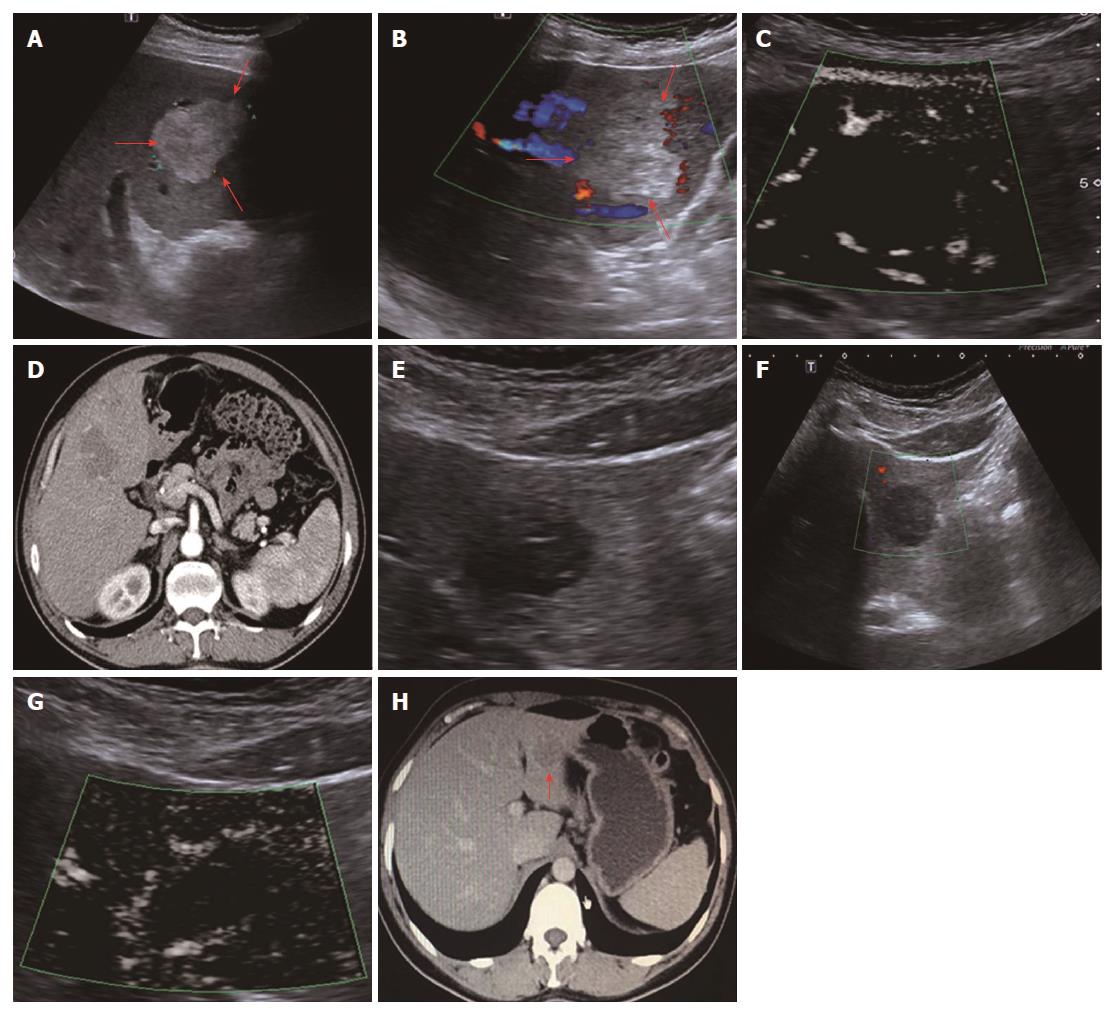
Figure 3 Strip rim type (type II).
A-D: A 61-year-old male diagnosed with hemangioma. A: A high-echo lesion with a clear margin was evident in the left liver lobe; B: CDFI showed an interrupted strip blood flow signal around the edge of this lesion; C: SMI showed a relatively continuous strip rim-distributed microvascular structure; D: Contrast-enhanced CT showed strip rim enhancement of the lesion in the arterial phase. E-H: A 63-year-old male diagnosed with hemangioma. E: A low-echo lesion with a clear margin was evident in the left liver lobe; F: CDFI showed no blood flow signal for this lesion; G: SMI showed a continuous strip rim microvascular structure; H: Contrast-enhanced CT showed strip rim enhancement of the lesion in the arterial phase. SMI: Superb microvascular imaging.
- Citation: He MN, Lv K, Jiang YX, Jiang TA. Application of superb microvascular imaging in focal liver lesions. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(43): 7765-7775
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i43/7765.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i43.7765