Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2017; 23(43): 7735-7745
Published online Nov 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i43.7735
Published online Nov 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i43.7735
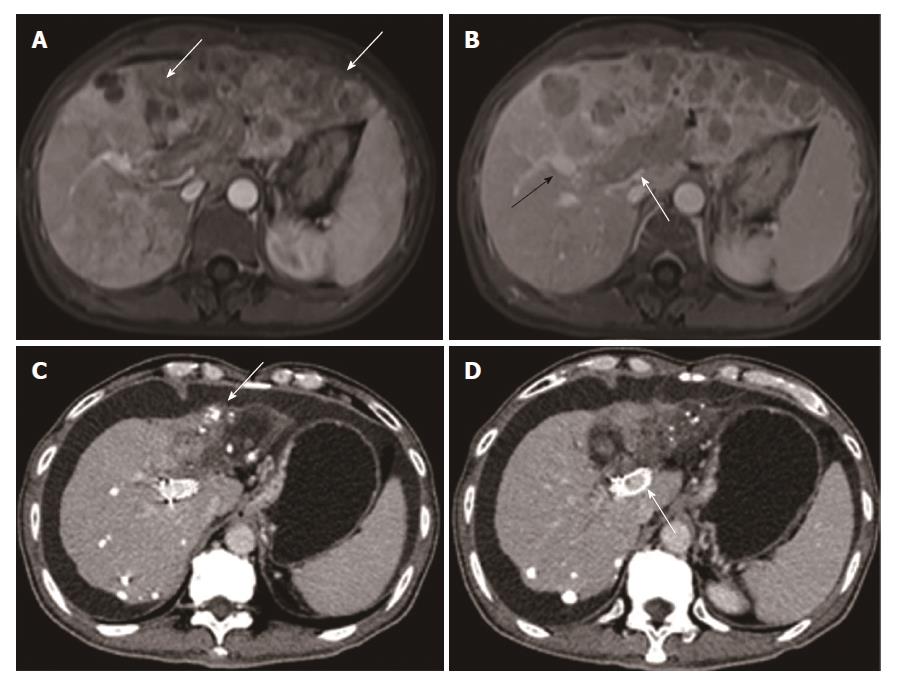
Figure 1 Images from a 50-year-old man who had hepatocellular carcinoma with main portal vein tumor thrombus.
A: Contrast-enhanced abdominal magnetic resonance imaging before therapy. Diffuse hepatocellular carcinoma (white arrow) was detected in the left lobe. B: The second order of the right portal vein (black arrow) was patent. Tumor thrombus (white arrow) was observed in the left portal vein, the first order of the right portal vein, and the main portal vein. C: Contrast-enhanced abdominal CT image 24 mo after first therapy. Deposition of iodized oil (white arrow) within tumor was observed and the left lobe was atrophied. D: The stent was still patent (white arrow).
- Citation: Zhang ZH, Liu QX, Zhang W, Ma JQ, Wang JH, Luo JJ, Liu LX, Yan ZP. Combined endovascular brachytherapy, sorafenib, and transarterial chemobolization therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma patients with portal vein tumor thrombus. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(43): 7735-7745
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i43/7735.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i43.7735