Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2017; 23(42): 7609-7617
Published online Nov 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i42.7609
Published online Nov 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i42.7609
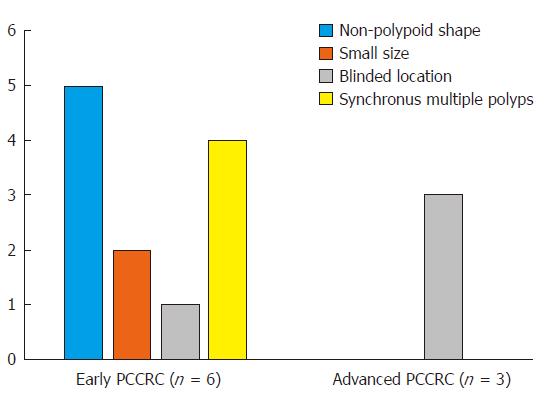
Figure 2 Possible explanations for the 9 “missed or new” post-colonoscopy colorectal cancers.
The bar chart shows the number of each possible explanation for the 6 early “missed or new” PCCRCs (left) and the 3 advanced “missed or new” PCCRCs (right). Among the 6 early “missed or new”PCCRCs, possible explanations were a non-polypoid shape in 5 cases (83%), presence of synchronous multiple (n ≥ 3) polyps at initial colonoscopy in 4 (67%), a small size (< 10 mm) in 2 (33%), and a blind location in 1 (17%). For all 3 (100%) of the advanced “missed or new” PCCRCs, a blind location was considered to have been likely. PCCRC: Post-colonoscopy colorectal cancer.
- Citation: Iwatate M, Kitagawa T, Katayama Y, Tokutomi N, Ban S, Hattori S, Hasuike N, Sano W, Sano Y, Tamano M. Post-colonoscopy colorectal cancer rate in the era of high-definition colonoscopy. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(42): 7609-7617
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i42/7609.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i42.7609