Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2017; 23(42): 7594-7608
Published online Nov 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i42.7594
Published online Nov 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i42.7594
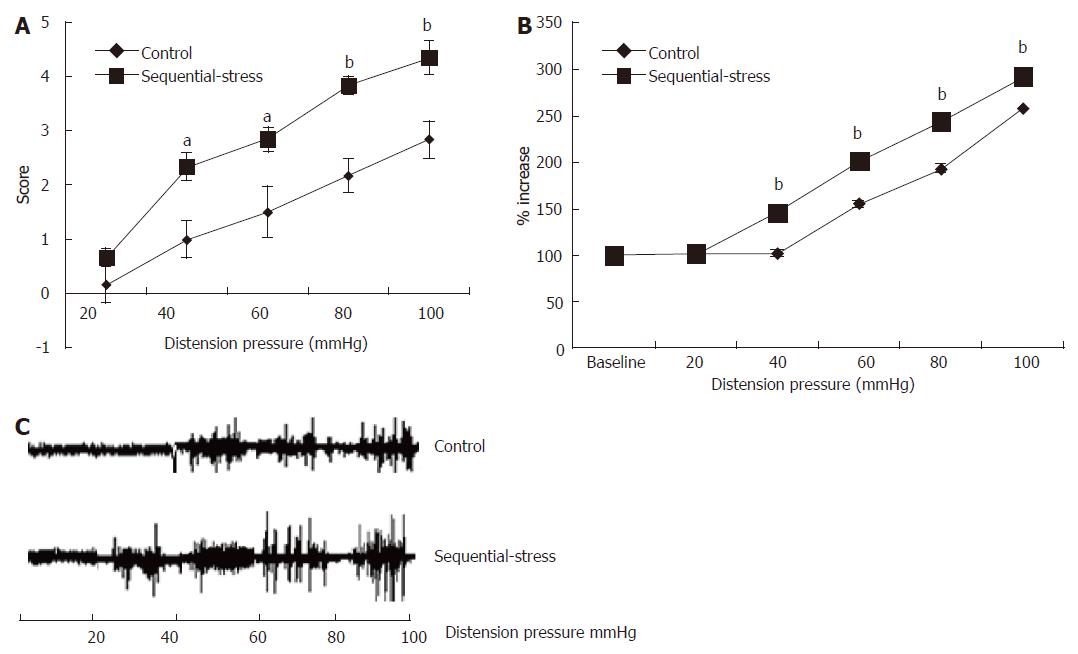
Figure 3 Abdominal withdrawal reflex and electromyographic tests showed the sequential-stress-treated rats exhibited gastric hypersensitivity to gastric distention.
A: AWR to GD of the sequential-stress-treated rats was significantly higher at the distention pressure 40, 60, 80 and 100 mmHg; B: EMG responses of the sequential-stress-treated rats were greater at the distention pressure 40, 60, 80 and 100 mmHg; C: The representative EMG response from both an adult sequential-stress-treated rat and control rat to GD. Data were expressed as the mean ± SEM of the AWR score and the percentage of EMG derived AUC increased (n = 8 in each group). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control group.
- Citation: Jing FC, Zhang J, Feng C, Nian YY, Wang JH, Hu H, Yang BD, Sun XM, Zheng JY, Yin XR. Potential rat model of anxiety-like gastric hypersensitivity induced by sequential stress. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(42): 7594-7608
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i42/7594.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i42.7594