Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2017; 23(42): 7505-7518
Published online Nov 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i42.7505
Published online Nov 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i42.7505
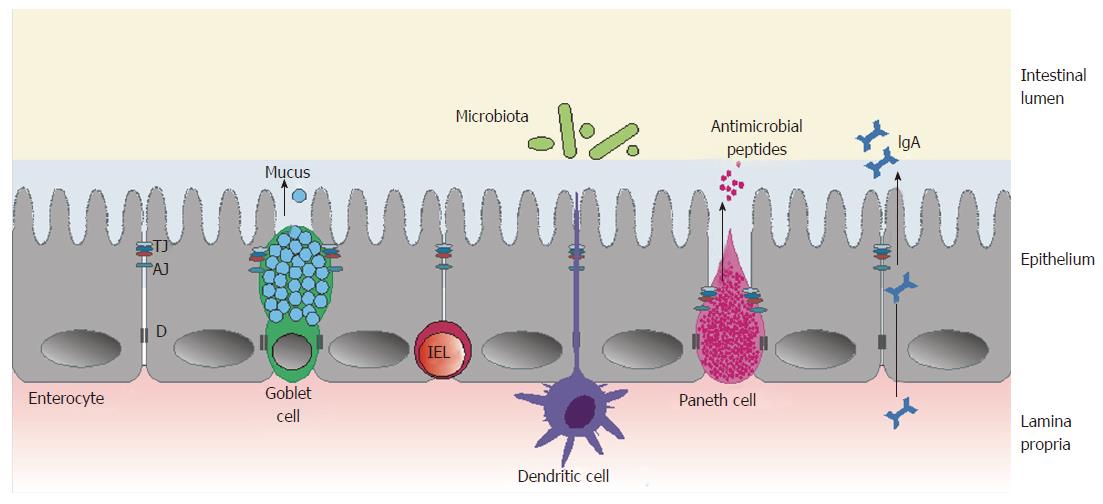
Figure 1 Schematic illustration of the intestinal barrier.
The three main components of the intestinal barrier: the microbiota; epithelium, with its specialized cells (goblet cells, Paneth cells and enterocytes), together with a layer of mucus; and gut-associated lymphoid tissue cells, including IELs and dendritic cells. AJ: Adherens junction; D: Desmosome; IEL: Intraepithelial lymphocyte; TJ: Tight junction.
- Citation: Cukrowska B, Sowińska A, Bierła JB, Czarnowska E, Rybak A, Grzybowska-Chlebowczyk U. Intestinal epithelium, intraepithelial lymphocytes and the gut microbiota - Key players in the pathogenesis of celiac disease. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(42): 7505-7518
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i42/7505.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i42.7505