Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2017; 23(40): 7253-7264
Published online Oct 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i40.7253
Published online Oct 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i40.7253
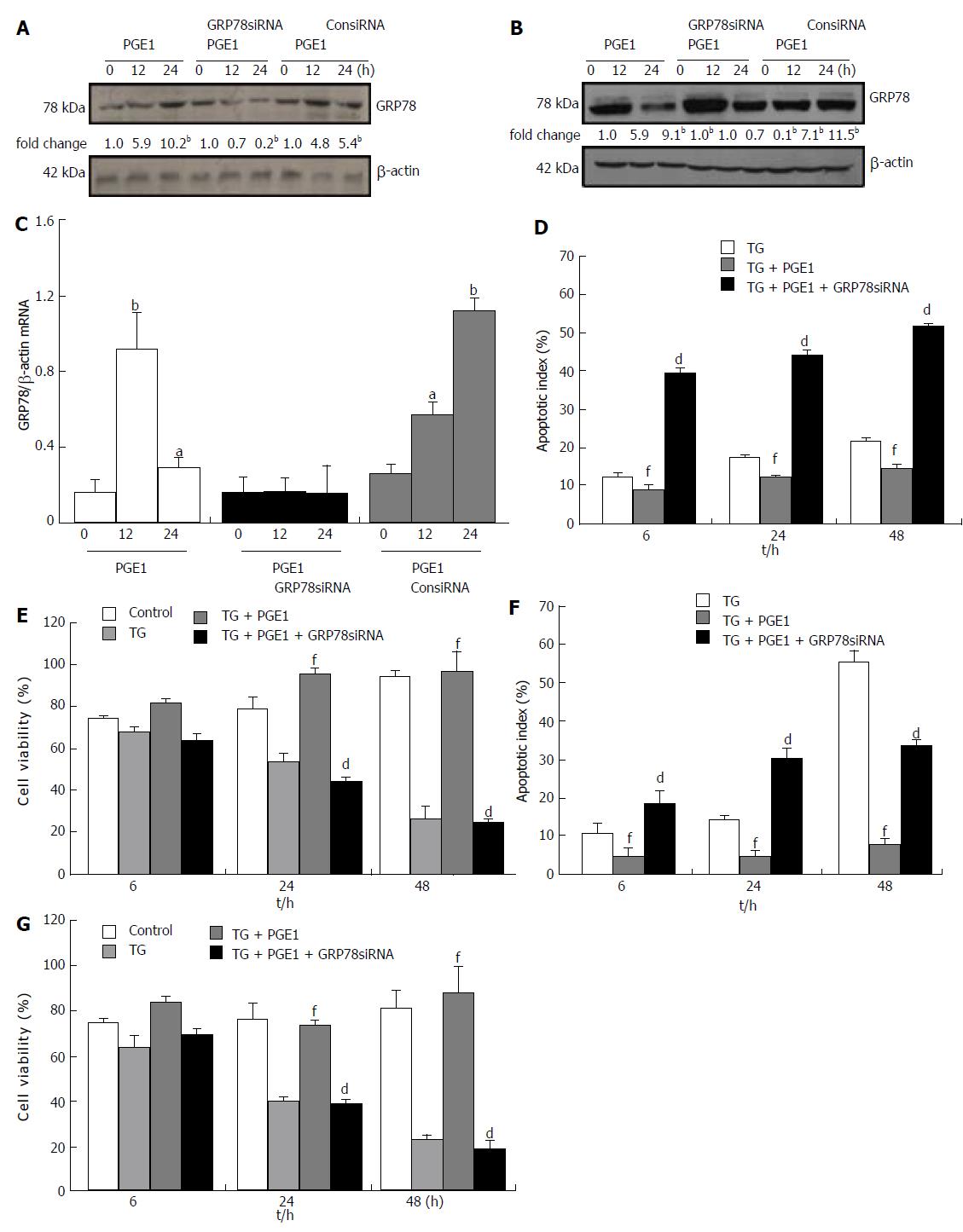
Figure 5 Prostaglandin E1 induced glucose-regulated protein 78 expression and protected L02 cells against endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis via a protein kinase a-dependent pathway.
A and B: L02 cells were pretreated with or without PKA inhibitor H89 (10 μmol/L) or KT5720 (1 μmol/L), and then 1 μmol/L PGE1 for 3, 6 and 12 h. The expressions of GRP78 were detected by western blotting. One representative blot each from three independent experiments is presented. The results of densitometric analysis are presented as a fold-change compared to those of PGE1 at the same time points (bP < 0.01); C: L02 cells were pretreated with or without 10 μmol/L H89, and then 1 μmol/L PGE1 and a final concentration of 1 μmol/L TG for 6, 24 and 48 h. The apoptotic index was determined by flow cytometry. Histograms represent mean ± SD of five separate experiments, each of which was performed in triplicate. (dP < 0.01 vs those of TG + PGE1 at the same time point; fP < 0.01 vs those of TG at the same time point); D: L02 cells were pretreated with or without 10 μmol/L H89, and then 1 μmol/L PGE1 and a final concentration of 1 μmol/L TG for 6, 24 and 48 h. Cell viability of L02 cells was determined by MTS assay. Histograms represent mean ± SD of five separate experiments, each of which was performed in triplicate (dP < 0.01 vs those of TG + PGE1 at the same time point; fP < 0.01 vs those of TG at the same time point). GRP78: Glucose-regulated protein 78; MTS: [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium]; PGE1: Prostaglandin E1; PKA: Protein kinase A; TG: Thapsigargin.
- Citation: Yang FW, Fu Y, Li Y, He YH, Mu MY, Liu QC, Long J, Lin SD. Prostaglandin E1 protects hepatocytes against endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis via protein kinase A-dependent induction of glucose-regulated protein 78 expression. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(40): 7253-7264
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i40/7253.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i40.7253