Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2017; 23(4): 712-722
Published online Jan 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i4.712
Published online Jan 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i4.712
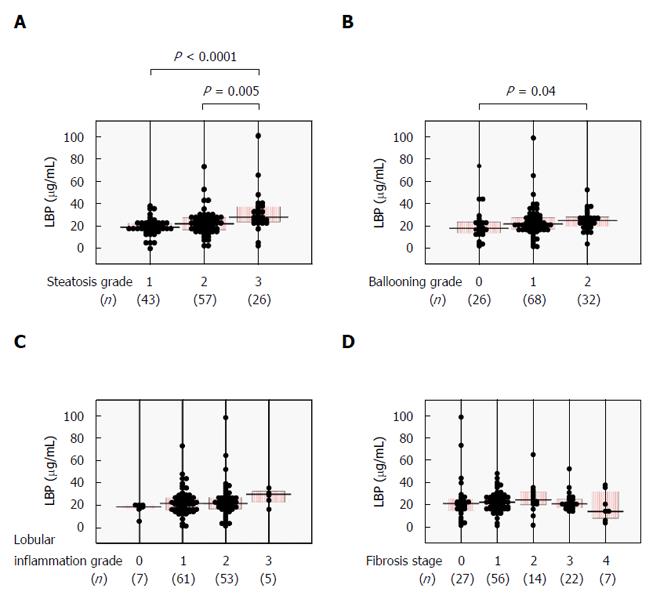
Figure 2 Relationships between serum lipopolysaccharide-binding protein and histological findings in 126 biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients.
A: Steatosis (1-3); B: Ballooning (0-2); C: Lobular inflammation (0-3); and D: Fibrosis (0-4) scores. Comparisons among subgroups were conducted using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s correction. LBP: Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein.
- Citation: Kitabatake H, Tanaka N, Fujimori N, Komatsu M, Okubo A, Kakegawa K, Kimura T, Sugiura A, Yamazaki T, Shibata S, Ichikawa Y, Joshita S, Umemura T, Matsumoto A, Koinuma M, Sano K, Aoyama T, Tanaka E. Association between endotoxemia and histological features of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(4): 712-722
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i4/712.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i4.712