Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2017; 23(39): 7139-7149
Published online Oct 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i39.7139
Published online Oct 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i39.7139
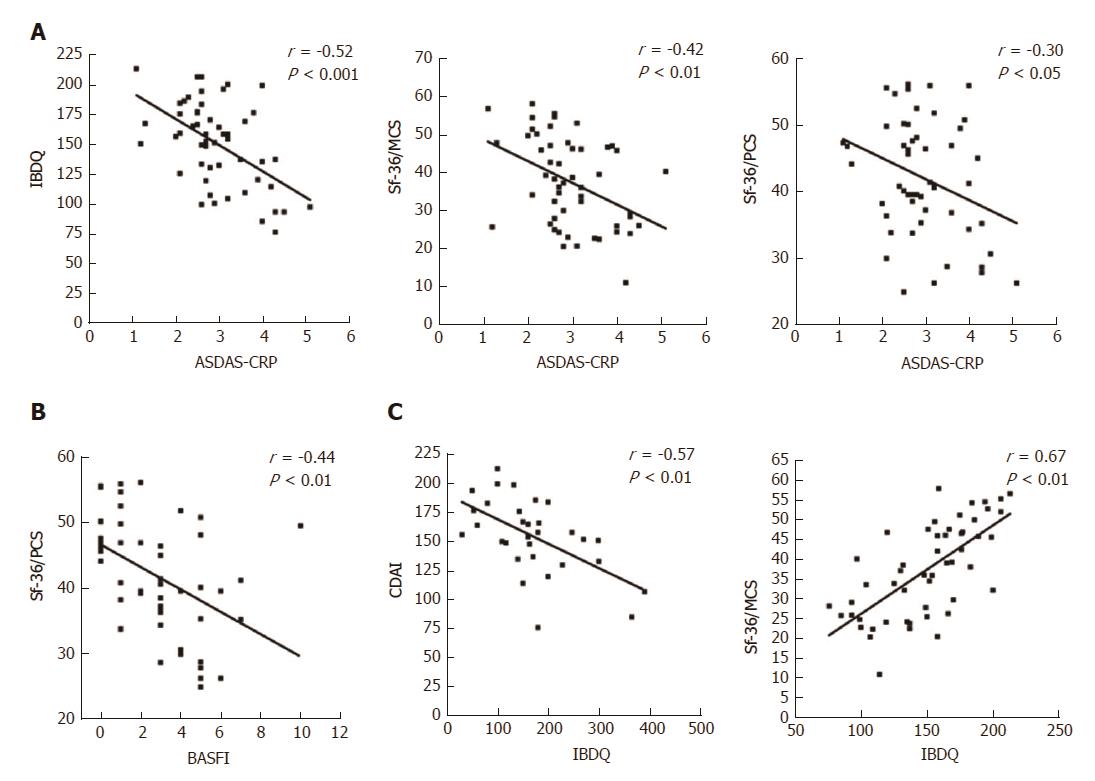
Figure 3 Correlations between articular and gastrointestinal disease activity and HRQoL scores in the ES-AN patient cohort at baseline.
A: Correlation between the PROs of gastrointestinal disease activity (assessed by IBQD) scores and SF-36 summary scores (assessed by PCS and MCS) with articular activity scores (assessed by ASDAS-CRP); B: Correlation of the articular function (assessed by BASFI with SF-36/PCS); C: Correlation of the IBDQ with crohn’s disease gastrointestinal disease activity (assessed by CDAI) and the SF-36/MCS. ASDAS-CRP: Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score-C-Reactive Protein; CDAI: Crohn’s Disease Activity Index; ES: Enteropathic spondyloarthritis; ES-AN: Patients affected by ES in the ancona’s cohort; HRQoL: Health-Related Quality of Life; IBDQ: Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire; PROs: Patient reported outcomes; SF-36/MCS: Summary of “Mental Component Score” of the Short Form-36 health survey; SF-36/PCS: Summary of “Physical Component Score” of the Short Form-36 health survey.
- Citation: Luchetti MM, Benfaremo D, Ciccia F, Bolognini L, Ciferri M, Farinelli A, Rossini M, Mosca P, Triolo G, Gabrielli A. Adalimumab efficacy in enteropathic spondyloarthritis: A 12-mo observational multidisciplinary study. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(39): 7139-7149
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i39/7139.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i39.7139