Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2017; 23(39): 7098-7109
Published online Oct 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i39.7098
Published online Oct 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i39.7098
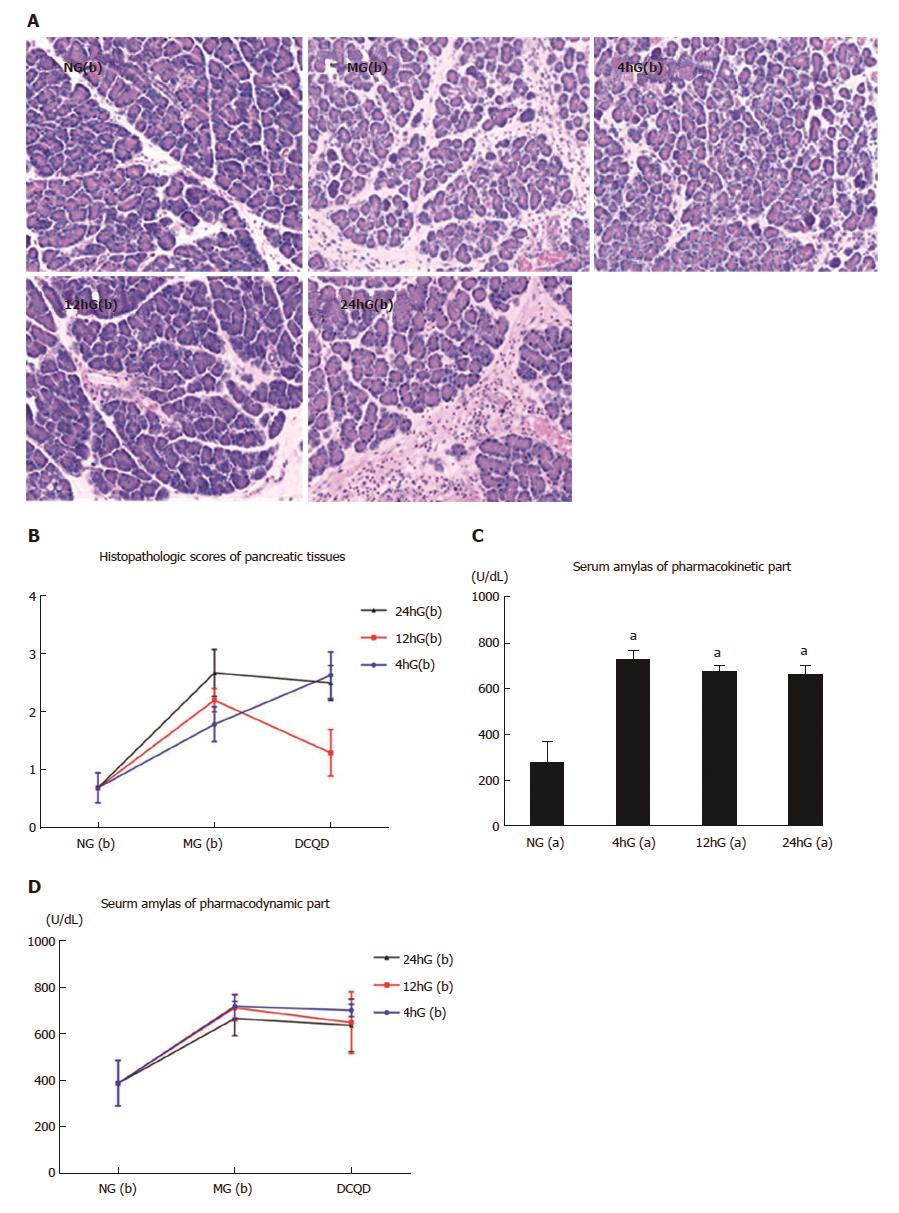
Figure 3 Pathological damages in the pancreatic tissues and changes in the serum amylase concentration.
Rats (n = 6 per group) were orally administered DCQD (10 mL/kg.BW) 4 h, 12 h and 24 h after AP induction. Pancreatic tissues were collected for staining with hematoxylin-eosin (A, × 200) 24 h after a single dosage of DCQD; B: Pathological scores of the pancreatic tissues. Serum amylase was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (C and D). The results are presented as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 vs NG(a). NG(a/b): the sham-operated group; MG(b): the model group or the control group; 4hG(a/b) 12hG(a/b), and 24hG(a/b): rats were orally dosed with DCQD 4 h, 12 h and 24 h, respectively, after AP induction. AP: Acute pancreatitis; DCQD: Da-Cheng-Qi decoction.
- Citation: Zhang YM, Zhu L, Zhao XL, Chen H, Kang HX, Zhao JL, Wan MH, Li J, Zhu L, Tang WF. Optimal timing for the oral administration of Da-Cheng-Qi decoction based on the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic targeting of the pancreas in rats with acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(39): 7098-7109
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i39/7098.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i39.7098