Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2017; 23(38): 6962-6972
Published online Oct 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i38.6962
Published online Oct 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i38.6962
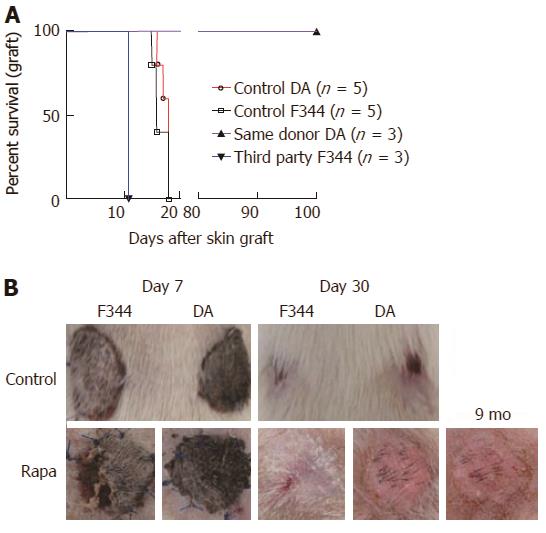
Figure 6 A short course of rapamycin induces antigen-specific tolerance.
Allogeneic liver transplantations were performed (DA donor to LEW recipients), and the rats were treated with a short course of rapamycin (1 mg/kg, days 4 to 11). On day 30 after liver transplantation, skin grafts were performed with skin from the same DA donor or from third-party F344 rats. The control groups received allogeneic skin grafts from DA or F344 donors with rats (LEW) that did not undergo liver transplantation. A: Cumulative survival curves; days indicate the days post-skin graft, n = 3-5 rats/group; B: Representative images are shown on day 7 and day 30 after skin grafts.
- Citation: Hamdani S, Thiolat A, Naserian S, Grondin C, Moutereau S, Hulin A, Calderaro J, Grimbert P, Cohen JL, Azoulay D, Pilon C. Delayed and short course of rapamycin prevents organ rejection after allogeneic liver transplantation in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(38): 6962-6972
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i38/6962.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i38.6962